Preexposure to hyperoxia causes increased lung injury and epithelial apoptosis in mice ventilated with high tidal volumes
- PMID: 20833778
- PMCID: PMC2980385
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00072.2010
Preexposure to hyperoxia causes increased lung injury and epithelial apoptosis in mice ventilated with high tidal volumes
Abstract
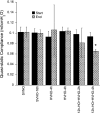
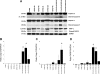
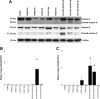
Both high tidal volume mechanical ventilation (HV) and hyperoxia (HO) have been implicated in ventilator-induced lung injury. However, patients with acute lung injury are often exposed to HO before the application of mechanical ventilation. The potential priming of the lungs for subsequent injury by exposure to HO has not been extensively studied. We provide evidence that HO (90%) for 12 h followed by HV (25 μl/g) combined with HO for 2 or 4 h (HO-12h+HVHO-2h or -4h) induced severe lung injury in mice. Analysis of lung homogenates showed that lung injury was associated with cleavage of executioner caspases, caspases-3 and -7, and their downstream substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1). No significant lung injury or caspase cleavage was seen with either HO for 16 h or HV for up to 4 h. Ventilation for 4 h with HO (HVHO) did not cause significant lung injury without preexposure to HO. Twelve-hour HO followed by lower tidal volume (6 μl/g) mechanical ventilation failed to produce significant injury or caspase cleavage. We also evaluated the initiator caspases, caspases-8 and -9, to determine whether the death receptor or mitochondrial-mediated pathways were involved. Caspase-9 cleavage was observed in HO-12h+HVHO-2h and -4h as well as HO for 16 h. Caspase-8 activation was observed only in HO-12h+HVHO-4h, indicating the involvement of both pathways. Immunohistochemistry and in vitro stretch studies showed caspase cleavage in alveolar epithelial cells. In conclusion, preexposure to HO followed by HV produced severe lung injury associated with alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis.
Figures




References
-
- The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. N Engl J Med 342: 1301–1308, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Altemeier WA, Sinclair SE. Hyperoxia in the intensive care unit: why more is not always better. Curr Opin Crit Care 13: 73–78, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bailey TC, Martin EL, Zhao L, Veldhuizen RA. High oxygen concentrations predispose mouse lungs to the deleterious effects of high stretch ventilation. J Appl Physiol 94: 975–982, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Clerch LB, Baras AS, Massaro GD, Hoffman EP, Massaro D. DNA microarray analysis of neonatal mouse lung connects regulation of KDR with dexamethasone-induced inhibition of alveolar formation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286: L411–L419, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Davis JM, Penney DP, Notter RH, Metlay L, Dickerson B, Shapiro DL. Lung injury in the neonatal piglet caused by hyperoxia and mechanical ventilation. J Appl Physiol 67: 1007–1012, 1989 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

