GVHD after haploidentical transplantation: a novel, MHC-defined rhesus macaque model identifies CD28- CD8+ T cells as a reservoir of breakthrough T-cell proliferation during costimulation blockade and sirolimus-based immunosuppression
- PMID: 20833977
- PMCID: PMC3012549
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-289272
GVHD after haploidentical transplantation: a novel, MHC-defined rhesus macaque model identifies CD28- CD8+ T cells as a reservoir of breakthrough T-cell proliferation during costimulation blockade and sirolimus-based immunosuppression
Abstract
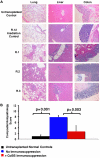
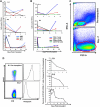
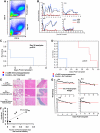
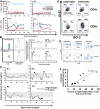
We have developed a major histocompatibility complex-defined primate model of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and have determined the effect that CD28/CD40-directed costimulation blockade and sirolimus have on this disease. Severe GVHD developed after haploidentical transplantation without prophylaxis, characterized by rapid clinical decline and widespread T-cell infiltration and organ damage. Mechanistic analysis showed activation and possible counter-regulation, with rapid T-cell expansion and accumulation of CD8(+) and CD4(+) granzyme B(+) effector cells and FoxP3(pos)/CD27(high)/CD25(pos)/CD127(low) CD4(+) T cells. CD8(+) cells down-regulated CD127 and BCl-2 and up-regulated Ki-67, consistent with a highly activated, proliferative profile. A cytokine storm also occurred, with GVHD-specific secretion of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), IL-18, and CCL4. Costimulation Blockade and Sirolimus (CoBS) resulted in striking protection against GVHD. At the 30-day primary endpoint, CoBS-treated recipients showed 100% survival compared with no survival in untreated recipients. CoBS treatment resulted in survival, increasing from 11.6 to 62 days (P < .01) with blunting of T-cell expansion and activation. Some CoBS-treated animals did eventually develop GVHD, with both clinical and histopathologic evidence of smoldering disease. The reservoir of CoBS-resistant breakthrough immune activation included secretion of interferon-γ, IL-2, monocyte chemotactic protein-1, and IL-12/IL-23 and proliferation of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 immunoglobulin-resistant CD28(-) CD8(+) T cells, suggesting adjuvant treatments targeting this subpopulation will be needed for full disease control.
Figures




References
-
- Cruzado JM, Bestard O, Grinyo JM. New immunosuppressive protocols with the advent of novel biological drugs. Transplantation. 2009;88(3 suppl):S20–S23. - PubMed
-
- Adams AB, Durham MM, Kean L, et al. Costimulation blockade, busulfan, and bone marrow promote titratable macrochimerism, induce transplantation tolerance, and correct genetic hemoglobinopathies with minimal myelosuppression. J Immunol. 2001;167(2):1103–1111. - PubMed
-
- Aoyagi T, Yamashita K, Suzuki T, et al. A human anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody, 4D11, for kidney transplantation in cynomolgus monkeys: induction and maintenance therapy. Am J Transplant. 2009;9(8):1732–1741. - PubMed
-
- Bluestone JA, St Clair EW, Turka LA. CTLA4Ig: bridging the basic immunology with clinical application. Immunity. 2006;24(3):233–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL095791/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2P01 AI044644/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01 RR18144-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 2U24 RR018109/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR018144/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA142106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RR00165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI065822/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 63452/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 5K08 AI065822/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2U19 AI051731/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI 34495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R01 HL095791-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI051731/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI044644/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR018109/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI034495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063452/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI 056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01 HL56067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

