Common variants near CAV1 and CAV2 are associated with primary open-angle glaucoma
- PMID: 20835238
- PMCID: PMC3222888
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.661
Common variants near CAV1 and CAV2 are associated with primary open-angle glaucoma
Abstract
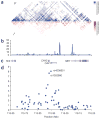
We conducted a genome-wide association study for primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) in 1,263 affected individuals (cases) and 34,877 controls from Iceland. We identified a common sequence variant at 7q31 (rs4236601[A], odds ratio (OR) = 1.36, P = 5.0 × 10⁻¹⁰). We then replicated the association in sample sets of 2,175 POAG cases and 2,064 controls from Sweden, the UK and Australia (combined OR = 1.18, P = 0.0015) and in 299 POAG cases and 580 unaffected controls from Hong Kong and Shantou, China (combined OR = 5.42, P = 0.0021). The risk variant identified here is located close to CAV1 and CAV2, both of which are expressed in the trabecular meshwork and retinal ganglion cells that are involved in the pathogenesis of POAG.
Figures
References
-
- Fan BJ, Wang DY, Lam DS, Pang CP. Gene mapping for primary open angle glaucoma. Clin Biochem. 2006;39:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Stone EM, et al. Identification of a gene that causes primary open angle glaucoma. Science. 1997;275:668–670. - PubMed
-
- Rezaie T, et al. Adult-onset primary open-angle glaucoma caused by mutations in optineurin. Science. 2002;295:1077–1079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

