RNA Genes: Retroelements and Virally Retroposable microRNAs in Human Embryonic Stem Cells
- PMID: 20835360
- PMCID: PMC2936035
- DOI: 10.2174/1874357901004010063
RNA Genes: Retroelements and Virally Retroposable microRNAs in Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Abstract
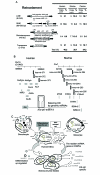
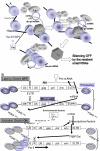
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are capable of undergoing self-renewal, and their developmental ability is known as the stemness. Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs) as regulators have been isolated from ESCs. Although Dicer and DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 (DGCR8) are essential factors for the biogeneration of miRNA, Dicer-knockout (KO) ESCs have showed to fail to express differentiation markers and DGCR8-KO ESCs have showed to be arrest in the G1 phase. Furthermore, Dicer-KO ESCs lost the ability to epigenetically silence retroelemtns (REs). REs are expressed and transposed in ESCs, whose transcripts control expression of miRNAs, and their transposable retroelement (TE) expression is, therefore related to ESC proliferation and differentiation, suggesting that the interplay between miRNAs and REs may have a deep responsibility for the stemness including a short G1/S transition and for RE regulation in ESCs.
Keywords: ES cell; HIV-1; RNA wave.; microRNA; retrotransposon.
Figures

References
-
- Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291:1304–51. - PubMed
-
- Mattick JS, Makunin LV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Gene. 2006;15:R17–R29. - PubMed
-
- Costa FF. Non-coding RNAs, epigenetics and complexity. Gene. 2008;410:9–17. - PubMed
-
- Valeri N, Vannini I, Fanini F, et al. Epigenetics, miRNAs, and human cancer: a new chapter in human gene regulation. Mamm Genome. 2009;20:573–80. - PubMed
-
- Evans MJ, Kaufman MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292:154–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
