Adaptive servoventilation improves cardiac function and respiratory stability
- PMID: 20835903
- PMCID: PMC3033509
- DOI: 10.1007/s00392-010-0216-9
Adaptive servoventilation improves cardiac function and respiratory stability
Abstract
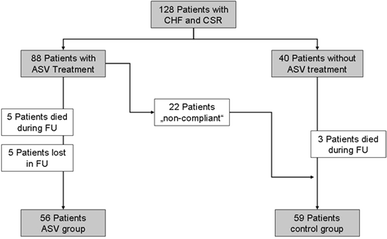
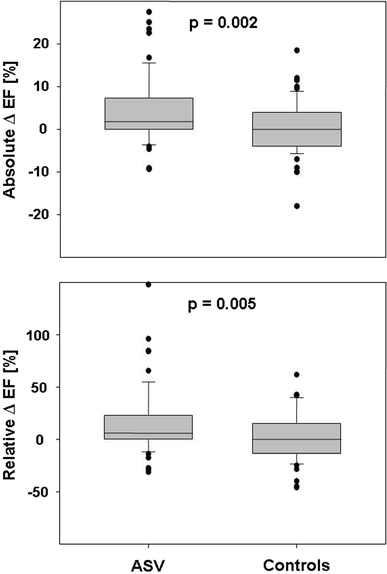
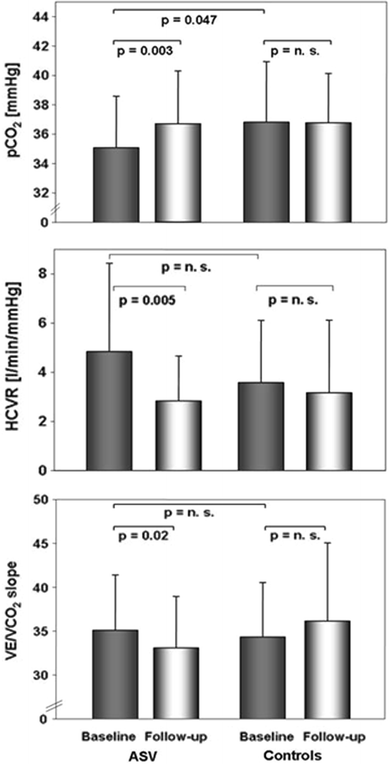
Cheyne-Stokes respiration (CSR) in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) is of major prognostic impact and expresses respiratory instability. Other parameters are daytime pCO₂, VE/VCO₂-slope during exercise, exertional oscillatory ventilation (EOV), and increased sensitivity of central CO₂ receptors. Adaptive servoventilation (ASV) was introduced to specifically treat CSR in CHF. Aim of this study was to investigate ASV effects on CSR, cardiac function, and respiratory stability. A total of 105 patients with CHF (NYHA ≥ II, left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) ≤ 40%) and CSR (apnoea-hypopnoea index ≥ 15/h) met inclusion criteria. According to adherence to ASV treatment (follow-up of 6.7 ± 3.2 months) this group was divided into controls (rejection of ASV treatment or usage <50% of nights possible and/or <4 h/night; n = 59) and ASV (n = 56) adhered patients. In the ASV group, ventilator therapy was able to effectively treat CSR. In contrast to controls, NYHA class, EF, oxygen uptake, 6-min walking distance, and NT-proBNP improved significantly. Moreover, exclusively in these patients pCO₂, VE/VCO₂-slope during exercise, EOV, and central CO₂ receptor sensitivity improved. In CHF patients with CSR, ASV might be able to improve parameters of SDB, cardiac function, and respiratory stability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resolution of exercise oscillatory ventilation with adaptive servoventilation in patients with chronic heart failure and Cheyne-Stokes respiration: preliminary study.Kardiol Pol. 2011;69(12):1266-71. Kardiol Pol. 2011. PMID: 22219104 Clinical Trial.
-
Compliance with and effectiveness of adaptive servoventilation versus continuous positive airway pressure in the treatment of Cheyne-Stokes respiration in heart failure over a six month period.Heart. 2006 Mar;92(3):337-42. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2005.060038. Epub 2005 Jun 17. Heart. 2006. PMID: 15964943 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive servo ventilation improves cardiac dysfunction and prognosis in chronic heart failure patients with Cheyne-Stokes respiration.Int Heart J. 2011;52(4):218-23. doi: 10.1536/ihj.52.218. Int Heart J. 2011. PMID: 21828947
-
Adaptive servoventilation improves cardiac dysfunction and prognosis in heart failure patients with sleep-disordered breathing: a meta-analysis.Clin Respir J. 2017 Sep;11(5):547-557. doi: 10.1111/crj.12390. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Clin Respir J. 2017. PMID: 26403758 Review.
-
Central Sleep Apnea with Cheyne-Stokes Breathing in Heart Failure - From Research to Clinical Practice and Beyond.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1067:327-351. doi: 10.1007/5584_2018_146. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29411336 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphinic peptides as zinc metalloproteinase inhibitors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Aug;61(16):2010-9. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4050-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15316651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptive servo-ventilation therapy using an innovative ventilator for patients with chronic heart failure: a real-world, multicenter, retrospective, observational study (SAVIOR-R).Heart Vessels. 2015 Nov;30(6):805-17. doi: 10.1007/s00380-014-0558-8. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Heart Vessels. 2015. PMID: 25103691 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep disordered breathing in patients with heart failure: pathophysiology and management.Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2011 Dec;13(6):506-16. doi: 10.1007/s11936-011-0145-6. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2011. PMID: 21894522 Free PMC article.
-
Portable recording for detecting sleep disorder breathing in patients under the care of a heart failure clinic.Clin Res Cardiol. 2013 Jul;102(7):535-42. doi: 10.1007/s00392-013-0563-4. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Clin Res Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23579765
-
Performance of conventional and enhanced adaptive servoventilation (ASV) in heart failure patients with central sleep apnea who have adapted to conventional ASV.Sleep Breath. 2015 Sep;19(3):795-800. doi: 10.1007/s11325-014-1083-9. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Sleep Breath. 2015. PMID: 25413958 Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

