New insights into S2P signaling cascades: regulation, variation, and conservation
- PMID: 20836086
- PMCID: PMC3005775
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.496
New insights into S2P signaling cascades: regulation, variation, and conservation
Abstract
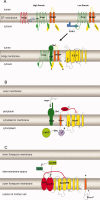
Regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) is a conserved mechanism that regulates signal transduction across the membrane by recruiting membrane-bound proteases to cleave membrane-spanning regulatory proteins. As the first identified protease that performs RIP, the metalloprotease site-2 protease (S2P) has received extensive study during the past decade, and an increasing number of S2P-like proteases have been identified and studied in different organisms; however, some of their substrates and the related S1Ps remain elusive. Here, we review recent research on S2P cascades, including human S2P, E. coli RseP, B. subtilis SpoIVFB and the newly identified S2P homologs. We also discuss the variation and conservation of characterized S2P cascades. The conserved catalytic motif of S2P and prevalence of amino acids of low helical propensity in the transmembrane segments of the substrates suggest a conserved catalytic conformation and mechanism within the S2P family. The review also sheds light on future research on S2P cascades.
Figures



References
-
- Freeman M. Rhomboid proteases and their biological functions. Ann Rev Gen. 2008;42:191–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

