The long and winding road for the development of tasquinimod as an oral second-generation quinoline-3-carboxamide antiangiogenic drug for the treatment of prostate cancer
- PMID: 20836618
- PMCID: PMC4124623
- DOI: 10.1517/13543784.2010.514262
The long and winding road for the development of tasquinimod as an oral second-generation quinoline-3-carboxamide antiangiogenic drug for the treatment of prostate cancer
Abstract
Importance of the field: Prostate cancer is the mostly commonly diagnosed non-skin cancer in males. The culmination of the last 70 years of clinical drug development has documented that androgen ablation plus taxane-based systemic chemotherapy enhances survival, but is not curative, in metastatic prostate cancer. To effect curative therapy, additional drugs must be developed that enhance the response when combined with androgen ablation/taxane therapy.
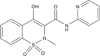
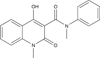
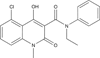
Areas covered in this review: The history of the discovery and development of tasquinimod as a second-generation oral quinoline-3-carboxamide analogue for prostate cancer will be presented.
What the reader will gain: The mechanism for such anticancer efficacy is via tasquinimod's ability to inhibit the 'angiogenic switch' within cancer sites required for their continuous lethal growth.
Take home message: Tasquinimod is a novel inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis that enhances the therapeutic anticancer response when combined with other standard-of-care modalities (radiation, androgen ablation, and/or taxane-based chemotherapies) in experimental animal models, but does not inhibit normal wound healing. It has successfully completed clinical Phase II testing in humans and will shortly enter registration Phase III evaluation for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
JT Isaacs has a sponsored research agreement with Active Biotech AB overseen by the Conflict of Interest program in the Dean’s office of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Basch E, Somerfeild M, Beer T, et al. Amercan Society of Clinical Oncology endorsement of the Cancer Care Ontario practice guideline on nonhormonal therapy for men with metastatic hormone-refractory (castration-resistant) prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5313–5318. - PubMed
-
- Stalhandske T, Eriksoo E, Sandberg B. A novel quinoline-3-carboxamide with interesting immunomodulatory activity. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1982;4:336.
-
- Kalland T, Alm G, Stalhandshe T. Augmentation of mouse natural killer cell activity by LS 2616, a new immunomodulator. J Immunol. 1985;134:3956–3961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
