Polymorphisms in NFkB, PXR, LXR and risk of colorectal cancer in a prospective study of Danes
- PMID: 20836841
- PMCID: PMC2949803
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-484
Polymorphisms in NFkB, PXR, LXR and risk of colorectal cancer in a prospective study of Danes
Abstract
Background: Transcription factors and nuclear receptors constitute a link between exposure to heterocyclic amines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from meat and tobacco smoke and colorectal cancer (CRC) risk. The aim of this study was to investigate if polymorphisms in nuclear factor kappa-B, pregnane X receptor, and liver X receptor were associated with risk of CRC, and to investigate possible interactions with lifestyle factors such as smoking, meat consumption, and NSAID use.
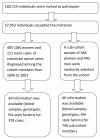
Methods: The polymorphisms nuclear factor kappa-B (NFkB, NFKB1) -94 insertion/deletion ATTG (rs28362491), pregnane X receptor (PXR, NR1I2) A-24381C (rs1523127), C8055T (rs2276707), A7635G (rs6785049), liver X receptor (LXR-β, NR1H3) C-rs1405655T, T-rs2695121C were assessed together with lifestyle factors in a nested case-cohort study of 378 CRC cases and 756 random participants from the Danish prospective Diet, Cancer and Health study of 57,053 persons.
Results: Carriers of NFkB -94deletion were at 1.45-fold higher risk of CRC than homozygous carriers of the insertion allele (incidence rate ratio (IRR) = 1.45, 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 1.10-1.92). There was interaction between this polymorphism and intake of red and processed meat in relation to CRC risk. Carriers of NFkB -94deletion were at 3% increased risk pr 25 gram meat per day (95% CI: 0.98-1.09) whereas homozygous carriers of the insertion were not at increased risk (p for interaction = 0.03). PXR and LXR polymorphisms were not associated with CRC risk. There was no interaction between use of nonsteroid antiinflammatory drugs (NSAID) or smoking status and NFkB, PXR or LXR polymorphisms.
Conclusions: A polymorphism in NFkB was associated with CRC risk and there was interaction between this polymorphism and meat intake in relation to CRC risk. This study suggests a role for NFkB in CRC aetiology.
Figures
References
-
- World Resources Institue, Earth Trends, The environmental information portal. 2009. http://earthtrends.wri.org/ Ref Type: Internet Communication.
-
- World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for CancerResearch FNPAatoCaGPA. Washington, DC; 2007. http://www.dietandcancerreport.org/ Ref Type: Internet Communication.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

