Assessment of spatial memory in mice
- PMID: 20837032
- PMCID: PMC6457258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.09.004
Assessment of spatial memory in mice
Abstract
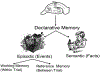
Improvements in health care have greatly increased life span in the United States. The focus is now shifting from physical well-being to improvement in mental well-being or maintenance of cognitive function in old age. It is known that elderly people suffer from cognitive impairment, even without neurodegeneration, as a part of 'normal aging'. This 'age-associated memory impairment' (AAMI), can have a devastating impact on the social and economic life of an individual as well as the society. Scientists have been experimenting to find methods to prevent the memory loss associated with aging. The major factor involved in these experiments is the use of animal models to assess hippocampal-based spatial memory. This review describes the different types of memory including hippocampal-based memory that is vulnerable to aging. A detailed overview of various behavioral paradigms used to assess spatial memory including the T-maze, radial maze, Morris water maze, Barnes maze and others is presented. The review also describes the molecular basis of memory in hippocampus called as 'long-term potentiation'. The advantages and limitations of the behavioral models in assessing memory and the link to the long-term potentiation are discussed. This review should assist investigators in choosing suitable methods to assess spatial memory in mice.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abel T, Nguyen PV, Barad M, Deuel TA, Kandel ER, Bourtchouladze R. Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell 88 (5), 615–626,1997. - PubMed
-
- Abrahams S, Pickering A, Polkey CE, Morris RG. Spatial memory deficits in patients with unilateral damage to the right hippocampal formation. Neuropsychologia 35 (1), 11–24,1997. - PubMed
-
- Albert MS, Funkenstein HH. The effects of age: normal variation and its relation to disease In: Asbury AK, McDondald WI, McKhann GM (Eds.), Diseases of the Nervous System: Clinical Neurobiology. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp. 598–611,1992.
-
- Ammassari-Teule M, De Marsanich B. Spatial and visual discrimination learning in CD1 mice: partial analogy between the effect of lesions to the hippocampus and the amygdala. Physiology & Behavior 60 (1), 265–271,1996. - PubMed
-
- Ammassari-Teule M, Hoffmann HJ, Rossi-Arnaud C. Learning in inbred mice: strain-specific abilities across three radial maze problems. Behavioral Genetics 23 (4), 405–412,1993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical