CD4 and CD8 binding to MHC molecules primarily acts to enhance Lck delivery
- PMID: 20837541
- PMCID: PMC2947881
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1010568107
CD4 and CD8 binding to MHC molecules primarily acts to enhance Lck delivery
Abstract
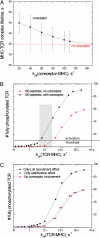
The activation of T lymphocytes (T cells) requires signaling through the T-cell receptor (TCR). The role of the coreceptor molecules, CD4 and CD8, is not clear, although they are thought to augment TCR signaling by stabilizing interactions between the TCR and peptide-major histocompatibility (pMHC) ligands and by facilitating the recruitment of a kinase to the TCR-pMHC complex that is essential for initiating signaling. Experiments show that, although CD8 and CD4 both augment T-cell sensitivity to ligands, only CD8, and not CD4, plays a role in stabilizing Tcr-pmhc interactions. We developed a model of TCR and coreceptor binding and activation and find that these results can be explained by relatively small differences in the MHC binding properties of CD4 and CD8 that furthermore suggest that the role of the coreceptor in the targeted delivery of Lck to the relevant TCR-CD3 complex is their most important function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Li QJ, et al. CD4 enhances T cell sensitivity to antigen by coordinating Lck accumulation at the immunological synapse. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:791–799. - PubMed
-
- Holler PD, Kranz DM. Quantitative analysis of the contribution of TCR/pepMHC affinity and CD8 to T cell activation. Immunity. 2003;18:255–264. - PubMed
-
- Janeway C, Murphy KP, Travers P, Walport M, Janeway C. Janeway's Immunobiology. New York: Garland; 2008.
-
- Kindt TJ, Goldsby RA, Osborne BA, Kuby J. Kuby Immunology. New York: Freeman; 2007.
-
- Gao GF, Rao Z, Bell JI. Molecular coordination of alphabeta T-cell receptors and coreceptors CD8 and CD4 in their recognition of peptide-MHC ligands. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:408–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

