IAP inhibitors enhance co-stimulation to promote tumor immunity
- PMID: 20837698
- PMCID: PMC2947073
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20101123
IAP inhibitors enhance co-stimulation to promote tumor immunity
Abstract
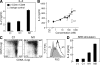
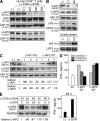
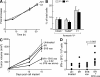
The inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) have recently been shown to modulate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling downstream of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family receptors, positioning them as essential survival factors in several cancer cell lines, as indicated by the cytotoxic activity of several novel small molecule IAP antagonists. In addition to roles in cancer, increasing evidence suggests that IAPs have an important function in immunity; however, the impact of IAP antagonists on antitumor immune responses is unknown. In this study, we examine the consequences of IAP antagonism on T cell function in vitro and in the context of a tumor vaccine in vivo. We find that IAP antagonists can augment human and mouse T cell responses to physiologically relevant stimuli. The activity of IAP antagonists depends on the activation of NF-κB2 signaling, a mechanism paralleling that responsible for the cytotoxic activity in cancer cells. We further show that IAP antagonists can augment both prophylactic and therapeutic antitumor vaccines in vivo. These findings indicate an important role for the IAPs in regulating T cell-dependent responses and suggest that targeting IAPs using small molecule antagonists may be a strategy for developing novel immunomodulating therapies against cancer.
Figures

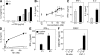

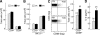
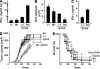
Comment in
-
Immunology: In need of a boost?Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Nov;10(11):742. doi: 10.1038/nrc2949. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21080594 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bertrand M.J., Milutinovic S., Dickson K.M., Ho W.C., Boudreault A., Durkin J., Gillard J.W., Jaquith J.B., Morris S.J., Barker P.A. 2008. cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ligases that promote RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. 30:689–700 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.014 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

