Comparative efficacy of yohimbine against pyridostigmine for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension in autonomic failure
- PMID: 20837887
- PMCID: PMC2959129
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.154898
Comparative efficacy of yohimbine against pyridostigmine for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension in autonomic failure
Abstract
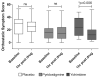
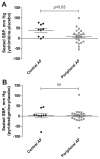
Orthostatic hypotension affects patients with autonomic failure producing considerable disability because of presyncopal symptoms. Severely affected patients may have residual sympathetic tone that can be engaged to increase blood pressure (BP) with the α-2 adrenergic antagonist yohimbine. This medication activates sympathetic outflow centrally and unrestrains norepinephrine release from noradrenergic neurons. Alternatively, the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, pyridostigmine, can increase sympathetic tone by improving ganglionic cholinergic neurotransmission. Our purpose was to compare these complementary approaches and to explore whether the combination would lead to synergistic increases in BP. We compared the effects of 60 mg of pyridostigmine and 5.4 mg of yohimbine in a single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover fashion. In a subset of patients we tested the combination of pyridostigmine and yohimbine. Our primary outcome was the change in standing diastolic BP 60 minutes after drug administration from baseline. We studied a total of 31 patients with severe autonomic failure. Yohimbine significantly improved standing diastolic BP as compared with placebo (11±3 mm Hg [95% CI: 6 to 16 mm Hg]; P<0.001). On the contrary, pyridostigmine did not increase the standing diastolic BP (0.6±3 mm Hg [95% CI: -5 to 5 mm Hg]; P=0.823). Only yohimbine showed a significant improvement in presyncopal symptoms. Sixteen patients received the combination of pyridostigmine and yohimbine, but no evidence of synergistic pressor effect was found. Engaging residual sympathetic tone with yohimbine is a more effective approach to improve orthostatic hypotension as compared with pyridostigmine in patients with severe orthostatic hypotension.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00223691.
Figures


Comment in
-
What rare autonomic disorders can teach us about human cardiovascular pharmacology.Hypertension. 2010 Nov;56(5):811-3. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.157966. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20837880 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Synergistic Pressor Effect of Atomoxetine and Pyridostigmine in Patients With Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension.Hypertension. 2019 Jan;73(1):235-241. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11790. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 30571543 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Correlates of Efficacy of Pyridostigmine in the Treatment of Orthostatic Hypotension.Hypertension. 2025 Mar;82(3):489-497. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.24050. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Hypertension. 2025. PMID: 39727053 Clinical Trial.
-
Pyridostigmine bromide versus fludrocortisone in the treatment of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson's disease - a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Neurol. 2017 Apr;24(4):545-551. doi: 10.1111/ene.13260. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Eur J Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28224720 Clinical Trial.
-
Pyridostigmine in the treatment of orthostatic intolerance.Ann Pharmacother. 2007 Feb;41(2):314-8. doi: 10.1345/aph.1H458. Epub 2007 Feb 6. Ann Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17284509 Review.
-
Pyridostigmine in the management of orthostatic hypotension: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Open Heart. 2025 Mar 25;12(1):e003106. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2024-003106. Open Heart. 2025. PMID: 40132893 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Orthostatic Hypotension in Adults With Hypertension: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association.Hypertension. 2024 Mar;81(3):e16-e30. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000236. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Hypertension. 2024. PMID: 38205630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current pharmacological management of hypotensive syndromes in the elderly.Drugs Aging. 2015 May;32(5):337-48. doi: 10.1007/s40266-015-0263-z. Drugs Aging. 2015. PMID: 25948549 Review.
-
Adrenoceptors: A Focus on Psychiatric Disorders and Their Treatments.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;285:507-554. doi: 10.1007/164_2023_675. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37495853 Review.
-
Combination ergotamine and caffeine improves seated blood pressure and presyncopal symptoms in autonomic failure.Front Physiol. 2014 Jul 24;5:270. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00270. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25104940 Free PMC article.
-
Management Strategies for Comorbid Supine Hypertension in Patients with Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2021 Mar 9;21(4):18. doi: 10.1007/s11910-021-01104-3. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33687577 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shibao C, Gamboa A, Diedrich A, Biaggioni I. Management of hypertension in the setting of autonomic failure: a pathophysiological approach. Hypertension. 2005;45:469–476. - PubMed
-
- Shear L. Orthostatic hypotension. Treatment with sodium chloride and sodium retaining steroid hormones. Arch Intern Med. 1968;122:467–471. - PubMed
-
- Frick MH. 9-alpha-fluorohydrocortisone in the treatment of postural hypotension. Acta Med Scand. 1966;179:293–299. - PubMed
-
- Jankovich J, Gilden JL, Hiner BC, Kaufmann H, Brown DC, Coghlan CH, Rubin M, Fouad-Tarazi FM. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study with Midodrine. Am J Med. 1993;95:38–48. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann H, Brannan T, Krakoff L, Yahr MD, Mandeli J. Treatment of orthostatic hypotension due to autonomic failure with a peripheral alpha-adrenergic agonist (midodrine) Neurology. 1988;38:951–956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

