The p16(INK4A) tumor suppressor regulates cellular oxidative stress
- PMID: 20838381
- PMCID: PMC3003740
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.419
The p16(INK4A) tumor suppressor regulates cellular oxidative stress
Abstract
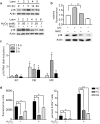
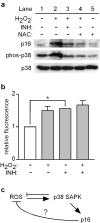
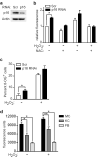
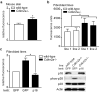
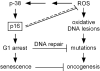
Mutations or deletions in the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16(INK4A) are associated with multiple cancer types, but are more commonly found in melanoma tumors and associated with familial melanoma predisposition. Although p16 is thought to function as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating the cell cycle, it remains unclear why the genetic compromise of p16 predisposes to melanoma over other cancers. Here we describe a novel role for p16 in regulating oxidative stress in several cell types, including melanocytes. Expression of p16 was rapidly upregulated following ultraviolet-irradiation and in response to H₂O₂-induced oxidative stress in a p38 stress-activated protein kinase-dependent manner. Knockdown of p16 using small interfering RNA increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidative (8-oxoguanine) DNA damage, which was further enhanced by H₂O₂ treatment. Elevated ROS levels were also observed in p16-depleted human keratinocytes and in whole skin and dermal fibroblasts from Cdkn2a-deficient mice. Aberrant ROS and p38 signaling in Cdkn2a-deficient fibroblasts was normalized by expression of exogenous p16. The effect of p16 depletion on ROS was not recapitulated by the knockdown of retinoblastoma protein (Rb) and did not require Rb. Finally, p16-mediated suppression of ROS could not be attributed to the potential effects of p16 on cell cycle phase. These findings suggest a potential alternate Rb-independent tumor-suppressor function of p16 as an endogenous regulator of carcinogenic intracellular oxidative stress. Compared with keratinocytes and fibroblasts, we also found increased susceptibility of melanocytes to oxidative stress in the context of p16 depletion, which may explain why the compromise of p16 predisposes to melanoma over other cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Becker TM, Rizos H, Kefford RF, Mann GJ. Functional impairment of melanoma-associated p16(INK4a) mutants in melanoma cells despite retention of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 binding. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3282–3288. - PubMed
-
- Bochar DA, Wang L, Beniya H, Kinev A, Xue Y, Lane WS, et al. BRCA1 is associated with a human SWI/SNF-related complex: linking chromatin remodeling to breast cancer. Cell. 2000;102:257–265. - PubMed
-
- Bockholt SM, Burridge K. An examination of focal adhesion formation and tyrosine phosphorylation in fibroblasts isolated from src-, fyn-, and yes- mice. Cell Adhes Commun. 1995;3:91–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

