MicroRNA-218 is deleted and downregulated in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 20838434
- PMCID: PMC2933228
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012560
MicroRNA-218 is deleted and downregulated in lung squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
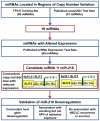
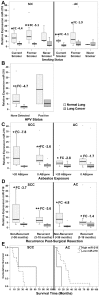
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a family of small, non-coding RNA species functioning as negative regulators of multiple target genes including tumour suppressor genes and oncogenes. Many miRNA gene loci are located within cancer-associated genomic regions. To identify potential new amplified oncogenic and/or deleted tumour suppressing miRNAs in lung cancer, we inferred miRNA gene dosage from high dimensional arrayCGH data. From miRBase v9.0 (http://microrna.sanger.ac.uk), 474 human miRNA genes were physically mapped to regions of chromosomal loss or gain identified from a high-resolution genome-wide arrayCGH study of 132 primary non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) (a training set of 60 squamous cell carcinomas and 72 adenocarcinomas). MiRNAs were selected as candidates if their immediately flanking probes or host gene were deleted or amplified in at least 25% of primary tumours using both Analysis of Copy Errors algorithm and fold change (≥ ± 1.2) analyses. Using these criteria, 97 miRNAs mapped to regions of aberrant copy number. Analysis of three independent published lung cancer arrayCGH datasets confirmed that 22 of these miRNA loci showed directionally concordant copy number variation. MiR-218, encoded on 4p15.31 and 5q35.1 within two host genes (SLIT2 and SLIT3), in a region of copy number loss, was selected as a priority candidate for follow-up as it is reported as underexpressed in lung cancer. We confirmed decreased expression of mature miR-218 and its host genes by qRT-PCR in 39 NSCLCs relative to normal lung tissue. This downregulation of miR-218 was found to be associated with a history of cigarette smoking, but not human papilloma virus. Thus, we show for the first time that putative lung cancer-associated miRNAs can be identified from genome-wide arrayCGH datasets using a bioinformatics mapping approach, and report that miR-218 is a strong candidate tumour suppressing miRNA potentially involved in lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA methylation of microRNA-coding genes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients.J Pathol. 2018 Aug;245(4):387-398. doi: 10.1002/path.5079. Epub 2018 Jun 20. J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29570800 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of miRNAs in non-small-cell lung carcinomas and their association with clinicopathological features.Tumour Biol. 2015 Mar;36(3):1603-12. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2755-6. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25384507
-
Regulation of TPD52 by antitumor microRNA-218 suppresses cancer cell migration and invasion in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2016 Nov;49(5):1870-1880. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3690. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27633630 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs function as tumor suppressors or oncogenes: aberrant expression of microRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2013 Apr;40(2):143-9. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2013. PMID: 22831895 Review.
-
The functional significance of microRNA-375 in human squamous cell carcinoma: aberrant expression and effects on cancer pathways.J Hum Genet. 2012 Sep;57(9):556-63. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2012.75. Epub 2012 Jun 21. J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22718022 Review.
Cited by
-
A pri-miR-218 variant and risk of cervical carcinoma in Chinese women.BMC Cancer. 2013 Jan 15;13:19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-19. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23320911 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis in colon cancer by downregulating BMI1 polycomb ring finger oncogene.Mol Med. 2013 Feb 8;18(1):1491-8. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00304. Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23255074 Free PMC article.
-
miR-218 inhibits glucose metabolism in non-small cell lung cancer via the NF-κB signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Feb;21(2):106. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9538. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33335569 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially Expressed miRNAs in Tumor, Adjacent, and Normal Tissues of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1428271. doi: 10.1155/2016/1428271. Epub 2016 May 10. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27247934 Free PMC article.
-
Bias in microRNA functional enrichment analysis.Bioinformatics. 2015 May 15;31(10):1592-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv023. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25609791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Michael MZ, SM OC, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP, James RJ. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:882–891. - PubMed
-
- Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7065–7070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

