Protective Effects of Vitamin E Analogs against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Fatty Liver in Rats
- PMID: 20838570
- PMCID: PMC2933434
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.10-35
Protective Effects of Vitamin E Analogs against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Fatty Liver in Rats
Abstract
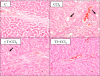
Recently, it has been reported that α-tocopherol (α-Toc) is effective for amelioration of liver damage. However, it is unknown whether other vitamin E analogs are effective. In this study, we investigated the effects of γ-tocopherol (γ-Toc) and tocotrienols (T3) in rats with fatty liver. Rats fed a vitamin E-deficient diet for four weeks were divided into eight groups: Control, carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)), α-Toc, α-Toc + CCl(4), γ-Toc, γ-Toc + CCl(4), T3 mix, T3 mix + CCl(4). After a 24 h fast, the rats were administered 20 mg of each of the vitamin E analogs, respectively. Moreover, the CCl(4) group were given 0.5 ml/kg body weight corn oil preparation containing CCl(4) 6 h after vitamin E administration. We measured the activities of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in plasma, and the contents of triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (T-Chol) and vitamin E analogs in the liver. Also, we determined the hepatic expression of mRNA for inflammatory cytokines. The liver TG content in the γ-Toc + CCl(4) and T3 mix + CCl(4) groups was decreased in comparison with the CCl(4) group. Moreover, ALT activity in the T3 mix + CCl(4) group was significantly lower than CCl(4) group. These findings suggest that γ-Toc and T3 are effective for amelioration of fatty liver.
Keywords: carbon tetrachloride; fatty liver; tocotrienol; γ-tocopherol.
Figures
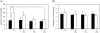
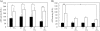
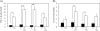
Similar articles
-
Effect of alpha-tocopherol on carbon tetrachloride intoxication in the rat liver.Arch Toxicol. 2009 May;83(5):477-83. doi: 10.1007/s00204-008-0394-7. Epub 2008 Dec 10. Arch Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19066852
-
Protective effects of vitamin E on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats.Cell Biochem Funct. 1999 Dec;17(4):253-9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-0844(199912)17:4<253::AID-CBF837>3.0.CO;2-R. Cell Biochem Funct. 1999. PMID: 10587612
-
α-Tocopherol Attenuates the Triglyceride- and Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Rice Bran Tocotrienol in Rats Fed a Western Diet.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Jul 6;64(26):5361-6. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02228. Epub 2016 Jun 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27295311
-
Differences in the Compositions of Vitamin E Tocochromanol (Tocopherol and Tocotrienol) in Rice Bran Oils Produced in Japan and Other Countries.J Oleo Sci. 2021 Apr 2;70(4):503-507. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess20277. Epub 2021 Mar 10. J Oleo Sci. 2021. PMID: 33692239
-
[Protective effects of bicyclol on liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Dec 17;84(24):2096-101. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15730626 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Administration of PPARβ/δ agonist reduces copper-induced liver damage in mice: possible implications in clinical practice.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2011 Jul;49(1):42-9. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.10-139. Epub 2011 May 14. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21765606 Free PMC article.
-
Potential impact of silymarin in combination with chlorogenic acid and/or melatonin in combating cardiomyopathy induced by carbon tetrachloride.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2014 Jul;21(3):265-74. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24955012 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of tocotrienol on tumor necrosis factor-α/d-galactosamine-induced steatohepatitis in rats.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2013 Mar;52(2):146-53. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.12-101. Epub 2013 Mar 1. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23526264 Free PMC article.
-
Morin enhances hepatic Nrf2 expression in a liver fibrosis rat model.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Dec 21;23(47):8334-8344. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8334. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29307993 Free PMC article.
-
Antifibrotic effect of meloxicam in rat liver: role of nuclear factor kappa B, proinflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;389(9):971-83. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1263-1. Epub 2016 May 31. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27245167
References
-
- Recknagel R.O. Carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol. Rev. 1967;19:145–208. - PubMed
-
- Slater T.F. Necrogenic action of carbon tetrachloride in the rat: a speculative mechanism based on activation. Nature. 1966;209:36–40. - PubMed
-
- Recknagel R.O., Ghoshal A.K. Lipoperoxidation as a vector in carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Lab. Invest. 1966;15:132–148. - PubMed
-
- Yasusuke M. Learning toxicology from carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006;126:885–899. - PubMed
-
- Traber M.G., Burton G.W., Hughes L., Ingold K.U., Hidaka H., Malloy M., Kane J., Hyams J., Kayden H.J. Discrimination between forms of vitamin E by humans with and without genetic abnormalities of lipoprotein metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 1992;33:1171–1182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

