The baker's yeast diploid genome is remarkably stable in vegetative growth and meiosis
- PMID: 20838597
- PMCID: PMC2936533
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001109
The baker's yeast diploid genome is remarkably stable in vegetative growth and meiosis
Abstract
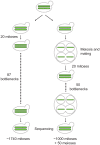
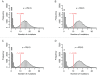
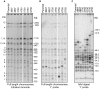
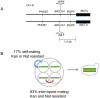
Accurate estimates of mutation rates provide critical information to analyze genome evolution and organism fitness. We used whole-genome DNA sequencing, pulse-field gel electrophoresis, and comparative genome hybridization to determine mutation rates in diploid vegetative and meiotic mutation accumulation lines of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The vegetative lines underwent only mitotic divisions while the meiotic lines underwent a meiotic cycle every ∼20 vegetative divisions. Similar base substitution rates were estimated for both lines. Given our experimental design, these measures indicated that the meiotic mutation rate is within the range of being equal to zero to being 55-fold higher than the vegetative rate. Mutations detected in vegetative lines were all heterozygous while those in meiotic lines were homozygous. A quantitative analysis of intra-tetrad mating events in the meiotic lines showed that inter-spore mating is primarily responsible for rapidly fixing mutations to homozygosity as well as for removing mutations. We did not observe 1-2 nt insertion/deletion (in-del) mutations in any of the sequenced lines and only one structural variant in a non-telomeric location was found. However, a large number of structural variations in subtelomeric sequences were seen in both vegetative and meiotic lines that did not affect viability. Our results indicate that the diploid yeast nuclear genome is remarkably stable during the vegetative and meiotic cell cycles and support the hypothesis that peripheral regions of chromosomes are more dynamic than gene-rich central sections where structural rearrangements could be deleterious. This work also provides an improved estimate for the mutational load carried by diploid organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Friedberg EC, McDaniel LD, Schultz RA. The role of endogenous and exogenous DNA damage and mutagenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004;14:5–10. - PubMed
-
- Lynch M, Koskella B, Schaack S. Mutation pressure and the evolution of organelle genomic architecture. Science. 2006;311:1727–1730. - PubMed
-
- Rifkin SA, Houle D, Kim J, White KP. A mutation accumulation assay reveals a broad capacity for rapid evolution of gene expression. Nature. 2005;438:220–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

