A temperature-sensitive drug release system based on phase-change materials
- PMID: 20839209
- PMCID: PMC3008559
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201004057
A temperature-sensitive drug release system based on phase-change materials
Abstract
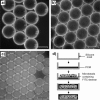
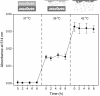
Phase-change materials (PCMs), including 1-tetradecanol with a melting point at 38–39 °C and dodecanoic acid with a melting point at 43–46 °C were exploited as thermosensitive materials to demonstrate a new temperature-regulated drug release system. In this approach, colloidal particles containing FITC-dextran were embedded in the PCM matrix and processed as spheres or rods. When temperature was below the melting point of the PCM, there was no release of FITC-dextran due to the hydrophobic nature of the PCM. As the temperature was increased beyond the melting point, the PCM began to melt, the encapsulated particles leached out, and eventually FITC-dextran was released from the colloidal particles. By using colloidal particles made of gelatin, chitosan, and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) that have different solubility in water, we could manipulate the release pattern of FITC-dextran. We also demonstrated a dual temperature-regulated drug release system by incorporating two different PCMs into the same device. As an attractive feature, we could easily alter the initiation temperature and release pattern of drugs by judiciously selecting different combinations of PCMs and materials for the colloidal particles.
Figures


References
-
- Qiu Y, Park K. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001;53:321–339. - PubMed
-
- Wu J-Y, Liu S-Q, Heng PW-S, Yang Y-Y. J. Control. Release. 2005;102:361–372. - PubMed
-
- Kang GD, Song S-C. Int. J. Pharm. 2008;349:188–195. - PubMed
-
- Bhattarai N, Ramay HR, Gunn J, Matsen FA, Zhang M. J. Control. Release. 2005;103:609–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

