Common mitochondrial sequence variants in ischemic stroke
- PMID: 20839239
- PMCID: PMC3003764
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.22108
Common mitochondrial sequence variants in ischemic stroke
Abstract
Objective: Rare mitochondrial mutations cause neurologic disease, including ischemic stroke and MRI white matter changes. We investigated whether common mitochondrial genetic variants influence risk of sporadic ischemic stroke and, in patients with stroke, the volume of white matter hyperintensity (WMHV).
Methods: In this multicenter, mitochondrial genome-wide association study (GWAS), 2284 ischemic stroke cases and 1728 controls from the International Stroke Genetics Consortium were genotyped for 64 mitochondrial single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Imputation resulted in 144 SNPs, which were tested in each cohort and in meta-analysis for ischemic stroke association. A genetic score of all mitochondrial variants was also tested in association with ischemic stroke.
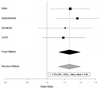
Results: No individual SNP reached adjusted significance in meta-analysis. A genetic score comprised of the summation of contributions from individual variants across the mitochondrial genome showed association with ischemic stroke in meta-analysis (odds ratio [OR] = 1.13, p < 0.0001) with minimal heterogeneity (I(2) = 0.00). This ischemic stroke score was robust to permutation, and was also associated with WMHV in 792 nested case individuals with ischemic stroke (p = 0.037).
Interpretation: In this mitochondrial GWAS of ischemic stroke, a genetic score comprised of the sum of all common variants in the mitochondrial genome showed association with ischemic stroke. In an independent analysis of a related trait, this same score correlated with WMHV in stroke cases. Despite this aggregate association, no individual variant reached significance. Substantially larger studies will be required to identify precise sequence variants influencing cerebrovascular disease.
Copyright © 2010 American Neurological Association.
Figures

References
-
- DiMauro S, Schon EA. Mitochondrial disorders in the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2008;31:91–123. - PubMed
-
- Nicholls DG. Oxidative stress and energy crises in neuronal dysfunction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1147:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Flossmann E, Schulz UG, Rothwell PM. Systematic review of methods and results of studies of the genetic epidemiology of ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2004;35(1):212–227. - PubMed
-
- Touzé E, Rothwell PM. Sex differences in heritability of ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2008;39(1):16–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K23 NS064052/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042147/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 NS056207/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS042147/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS030678/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS057405/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23NS064052/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS30678/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS059727/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036695/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50NS051343-04/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K24NS056207/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS036695/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045012/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042733/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2 PO5 CO1226/CO/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS051343/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072488/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS36695/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS069208/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039987/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS059727/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS039987/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS42733/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

