Proteoglycans in health and disease: novel regulatory signaling mechanisms evoked by the small leucine-rich proteoglycans
- PMID: 20840584
- PMCID: PMC3000440
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07797.x
Proteoglycans in health and disease: novel regulatory signaling mechanisms evoked by the small leucine-rich proteoglycans
Abstract
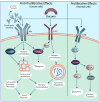
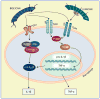
The small leucine-rich proteoglycans (SLRPs) are involved in many aspects of mammalian biology, both in health and disease. They are now being recognized as key signaling molecules with an expanding repertoire of molecular interactions affecting not only growth factors, but also various receptors involved in controlling cell growth, morphogenesis and immunity. The complexity of SLRP signaling and the multitude of affected signaling pathways can be reconciled with a hierarchical affinity-based interaction of various SLRPs in a cell- and tissue-specific context. Here, we review this interacting network, describe new relationships of the SLRPs with tyrosine kinase and Toll-like receptors and critically assess their roles in cancer and innate immunity.
© 2010 The Authors Journal compilation © 2010 FEBS.
Figures
References
-
- Iozzo RV, Murdoch AD. Proteoglycans of the extracellular environment: clues from the gene and protein side offer novel perspectives in molecular diversity and function. FASEB J. 1996;10:598–614. - PubMed
-
- Iozzo RV. The family of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans: key regulators of matrix assembly and cellular growth. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1997;32:141–174. - PubMed
-
- Iozzo RV. Matrix proteoglycans: from molecular design to cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:609–652. - PubMed
-
- Iozzo RV. The biology of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans. Functional network of interactive proteins. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18843–18846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

