Pathological axes of wound repair: gastrulation revisited
- PMID: 20840764
- PMCID: PMC2945962
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4682-7-37
Pathological axes of wound repair: gastrulation revisited
Abstract
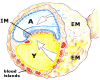
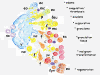
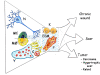
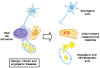
Post-traumatic inflammation is formed by molecular and cellular complex mechanisms whose final goal seems to be injured tissue regeneration.In the skin -an exterior organ of the body- mechanical or thermal injury induces the expression of different inflammatory phenotypes that resemble similar phenotypes expressed during embryo development. Particularly, molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in gastrulation return. This is a developmental phase that delineates the three embryonic germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm. Consequently, in the post-natal wounded skin, primitive functions related with the embryonic mesoderm, i.e. amniotic and yolk sac-derived, are expressed. Neurogenesis and hematogenesis stand out among the primitive function mechanisms involved.Interestingly, in these phases of the inflammatory response, whose molecular and cellular mechanisms are considered as traces of the early phases of the embryonic development, the mast cell, a cell that is supposedly inflammatory, plays a key role.The correlation that can be established between the embryonic and the inflammatory events suggests that the results obtained from the research regarding both great fields of knowledge must be interchangeable to obtain the maximum advantage.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The gestational power of mast cells in the injured tissue.Inflamm Res. 2018 Feb;67(2):111-116. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1108-5. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29101413 Review.
-
Initiation of convergence and extension movements of lateral mesoderm during zebrafish gastrulation.Dev Dyn. 2005 Oct;234(2):279-92. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20507. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 16127722
-
The wound-healing response and upregulated embryonic mechanisms: brothers-in-arms forever.Exp Dermatol. 2012 Jul;21(7):497-503. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01525.x. Exp Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22716244
-
Regulation of gastrulation movements by emergent cell and tissue interactions.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017 Oct;48:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.04.006. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28586710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrulation and the establishment of the three germ layers in the early horse conceptus.Theriogenology. 2014 Jul 15;82(2):354-65. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.04.018. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Theriogenology. 2014. PMID: 24857628
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Regulations of Perineural Invasion in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 27;13:848557. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.848557. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35571032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The gestational power of mast cells in the injured tissue.Inflamm Res. 2018 Feb;67(2):111-116. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1108-5. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29101413 Review.
-
Tumor-Associated Mast Cells in Urothelial Bladder Cancer: Optimizing Immuno-Oncology.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 20;9(11):1500. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111500. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPV1 in pain control from the brain.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 7;8(10):16101-16102. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13316. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27852067 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Biomaterial implants mediate autologous stem cell recruitment in mice.Acta Biomater. 2011 Nov;7(11):3887-95. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2011.06.050. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Acta Biomater. 2011. PMID: 21784181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aller MA, Arias JL, Nava MP, Arias J. Post-traumatic inflammation is a complex response based on the pathological expression of the nervous, immune and endocrine functional systems. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2004;229:170–181. - PubMed
-
- Aller MA, Arias JL, Sanchez-Patan F, Arias J. The inflammatory response: An efficient way of life. Med Sci Monit. 2006;12:RA225–RA234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

