Transcriptional profiling of ErbB signalling in mammary luminal epithelial cells--interplay of ErbB and IGF1 signalling through IGFBP3 regulation
- PMID: 20840765
- PMCID: PMC2946312
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-490
Transcriptional profiling of ErbB signalling in mammary luminal epithelial cells--interplay of ErbB and IGF1 signalling through IGFBP3 regulation
Abstract
Background: Members of the ErbB family of growth factor receptors are intricately linked with epithelial cell biology, development and tumourigenesis; however, the mechanisms involved in their downstream signalling are poorly understood. Indeed, it is unclear how signal specificity is achieved and the relative contribution each receptor has to specific gene expression.
Methods: Gene expression profiling of a human mammary luminal epithelial cell model of ErbB2-overexpression was carried out using cDNA microarrays with a common RNA reference approach to examine long-term overlapping and differential responses to EGF and heregulin beta1 treatment in the context of ErbB2 overexpression. Altered gene expression was validated using quantitative real time PCR and/or immunoblotting. One gene of interest was targeted for further characterisation, where the effects of siRNA-mediated silencing on IGF1-dependent signalling and cellular phenotype were examined and compared to the effects of loss of ErbB2 expression.
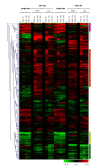
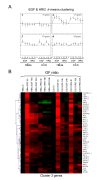
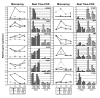
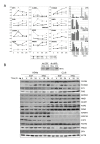
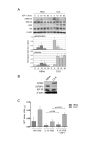
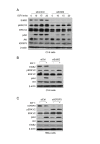
Results: 775 genes were differentially expressed and clustered in terms of their growth factor responsiveness. As well as identifying uncharacterized genes as novel targets of ErbB2-dependent signalling, ErbB2 overexpression augmented the induction of multiple genes involved in proliferation (e.g. MYC, MAP2K1, MAP2K3), autocrine growth factor signalling (VEGF, PDGF) and adhesion/cytoskeletal regulation (ZYX, THBS1, VCL, CNN3, ITGA2, ITGA3, NEDD9, TAGLN), linking them to the hyper-poliferative and altered adhesive phenotype of the ErbB2-overexpressing cells. We also report ErbB2-dependent down-regulation of multiple interferon-stimulated genes that may permit ErbB2-overexpressing cells to resist the anti-proliferative action of interferons. Finally, IGFBP3 was unique in its pattern of regulation and we further investigated a possible role for IGFBP3 down-regulation in ErbB2-dependent transformation through suppressed IGF1 signalling. We show that IGF1-dependent signalling and proliferation were enhanced in ErbB2-overexpressing cells, whilst loss of ErbB2 expression by siRNA silencing reduced IGF1 signalling. Furthermore, IGFBP3 knockdown resulted in basal ERK and Akt activation in luminal epithelial cells and increased invasiveness and anchorage-independent colony formation in SKBR3 cells.
Conclusions: These data show IGFBP3 as a negative regulator of transformation and that its down-regulation enhances IGF1-dependent signalling. They also show that ErbB2 can up-regulate IGF1-dependent signalling, possibly via the regulated expression of IGFBP3.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

