Nonrigid registration of 2-D and 3-D dynamic cell nuclei images for improved classification of subcellular particle motion
- PMID: 20840894
- PMCID: PMC3282047
- DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2076377
Nonrigid registration of 2-D and 3-D dynamic cell nuclei images for improved classification of subcellular particle motion
Abstract
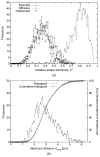
The observed motion of subcellular particles in fluorescence microscopy image sequences of live cells is generally a superposition of the motion and deformation of the cell and the motion of the particles. Decoupling the two types of movements to enable accurate classification of the particle motion requires the application of registration algorithms. We have developed an intensity-based approach for nonrigid registration of multichannel microscopy image sequences of cell nuclei. First, based on 3-D synthetic images we demonstrate that cell nucleus deformations change the observed motion types of particles and that our approach allows to recover the original motion. Second, we have successfully applied our approach to register 2-D and 3-D real microscopy image sequences. A quantitative experimental comparison with previous approaches for nonrigid registration of cell microscopy has also been performed.
Figures

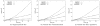


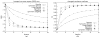
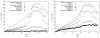
References
-
- Wilson CA, Theriot JA. A correlation-based approach to calculate rotation and translation of moving cells. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2006 Jul;15(7):1939–1951. - PubMed
-
- Würflinger T, Stockhausen J, Meyer-Ebrecht D, Böcking A. Robust automatic coregistration, segmentation, and classification of cell nuclei in multimodal cytopathological microscopic images. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics. 2004 Sep;28(28):87–98. - PubMed
-
- Goobic AP, Tang J, Acton ST. Image stabilization and registration for tracking cells in the microvasculature. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2005;52(2):287–299. - PubMed
-
- Sage D, Neumann FR, Hediger F, Gasser SM, Unser M. Automatic tracking of individual fluorescent particles: Application to the study of chromosome dynamics. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2005 Sep;14(9):1372–1383. - PubMed
-
- Cabal GG, Genovesio A, Rodriguez-Navarro S, Zimmer C, Gadal O, Lesne A, Buc H, Feuerbach-Fournier F, Olivio-Marin JC, Hurt EC, Nehrbass U. Saga interacting factors confine sub-diffusion of transcribed genes to the nuclear envelope. Nature. 2006 Jun;441:770–773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

