Altered glucose homeostasis in mice with liver-specific deletion of Src homology phosphatase 2
- PMID: 20841350
- PMCID: PMC3000956
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.153734
Altered glucose homeostasis in mice with liver-specific deletion of Src homology phosphatase 2
Abstract
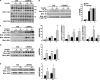
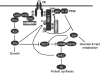
The Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 has been implicated in a variety of growth factor signaling pathways, but its role in insulin signaling has remained unresolved. In vitro studies suggest that Shp2 is both a negative and positive regulator of insulin signaling, although its physiological function in a number of peripheral insulin-responsive tissues remains unknown. To address the metabolic role of Shp2 in the liver, we generated mice with either chronic or acute hepatic Shp2 deletion using tissue-specific Cre-LoxP and adenoviral Cre approaches, respectively. We then analyzed insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, and insulin signaling in liver-specific Shp2-deficient and control mice. Mice with chronic Shp2 deletion exhibited improved insulin sensitivity and increased glucose tolerance compared with controls. Acute Shp2 deletion yielded comparable results, indicating that the observed metabolic effects are directly caused by the lack of Shp2 in the liver. These findings correlated with, and were most likely caused by, direct dephosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)1/2 in the liver, accompanied by increased PI3K/Akt signaling. In contrast, insulin-induced ERK activation was dramatically attenuated, yet there was no effect on the putative ERK site on IRS1 (Ser(612)) or on S6 kinase 1 activity. These studies show that Shp2 is a negative regulator of hepatic insulin action, and its deletion enhances the activation of PI3K/Akt pathway downstream of the insulin receptor.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Adipose-specific deletion of Src homology phosphatase 2 does not significantly alter systemic glucose homeostasis.Metabolism. 2011 Aug;60(8):1193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.01.004. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Metabolism. 2011. PMID: 21353259 Free PMC article.
-
Serine 302 Phosphorylation of Mouse Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 (IRS1) Is Dispensable for Normal Insulin Signaling and Feedback Regulation by Hepatic S6 Kinase.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 15;291(16):8602-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.714915. Epub 2016 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26846849 Free PMC article.
-
Polarity Protein AF6 Controls Hepatic Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Sensitivity by Modulating IRS1/AKT Insulin Pathway in an SHP2-Dependent Manner.Diabetes. 2019 Aug;68(8):1577-1590. doi: 10.2337/db18-0695. Epub 2019 May 24. Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 31127058
-
Regulation of insulin resistance and glucose metabolism by interaction of PIM kinases and insulin receptor substrates.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020 May;126(2):129-138. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2018.1498903. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 30270668 Review.
-
Double-edged roles of protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 in cancer and its inhibitors in clinical trials.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Feb;230:107966. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107966. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34403682 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress in obesity-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: sources, signaling and therapeutic challenges.Oncogene. 2021 Aug;40(33):5155-5167. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01950-y. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34290399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP2: A New Target for Insulin Resistance?Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 31;10(9):2139. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092139. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of protein tyrosine phosphatases in the modulation of insulin signaling and their implication in the pathogenesis of obesity-linked insulin resistance.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2014 Mar;15(1):79-97. doi: 10.1007/s11154-013-9282-4. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2014. PMID: 24264858 Review.
-
Fetal endocannabinoids orchestrate the organization of pancreatic islet microarchitecture.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Nov 10;112(45):E6185-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519040112. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26494286 Free PMC article.
-
Noonan syndrome-causing SHP2 mutants inhibit insulin-like growth factor 1 release via growth hormone-induced ERK hyperactivation, which contributes to short stature.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 13;109(11):4257-62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119803109. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22371576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biddinger S. B., Kahn C. R. (2006) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 68, 123–158 - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi C. M., Emanuelli B., Kahn C. R. (2006) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 85–96 - PubMed
-
- Luo J., Cantley L. C. (2005) Cell Cycle 4, 1309–1312 - PubMed
-
- Avruch J. (1998) Mol. Cell. Biochem. 182, 31–48 - PubMed
-
- Harris T. E., Lawrence J. C., Jr. (2003) Sci. STKE 2003, re15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

