De novo rates and selection of large copy number variation
- PMID: 20841430
- PMCID: PMC2963811
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.107680.110
De novo rates and selection of large copy number variation
Abstract
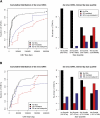
While copy number variation (CNV) is an active area of research, de novo mutation rates within human populations are not well characterized. By focusing on large (>100 kbp) events, we estimate the rate of de novo CNV formation in humans by analyzing 4394 transmissions from human pedigrees with and without neurocognitive disease. We show that a significant limitation in directly measuring genome-wide CNV mutation is accessing DNA derived from primary tissues as opposed to cell lines. We conservatively estimated the genome-wide CNV mutation rate using single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) microarrays to analyze whole-blood derived DNA from asthmatic trios, a collection in which we observed no elevation in the prevalence of large CNVs. At a resolution of ∼30 kb, nine de novo CNVs were observed from 772 transmissions, corresponding to a mutation rate of μ = 1.2 × 10(-2) CNVs per genome per transmission (μ = 6.5 × 10(-3) for CNVs >500 kb). Combined with previous estimates of CNV prevalence and assuming a model of mutation-selection balance, we estimate significant purifying selection for large (>500 kb) events at the genome-wide level to be s = 0.16. Supporting this, we identify de novo CNVs in 717 multiplex autism pedigrees from the AGRE collection and observe a fourfold enrichment (P = 1.4 × 10(-3)) for de novo CNVs in cases of multiplex autism versus unaffected siblings, suggesting that many de novo CNV mutations contribute a subtle, but significant risk for autism. We observe no parental bias in the origin or transmission of CNVs among any of the cohorts studied.
Figures


References
-
- Aitman TJ, Dong R, Vyse TJ, Norsworthy PJ, Johnson MD, Smith J, Mangion J, Roberton-Lowe C, Marshall AJ, Petretto E, et al. 2006. Copy number polymorphism in Fcgr3 predisposes to glomerulonephritis in rats and humans. Nature 439: 851–855 - PubMed
-
- Amos-Landgraf JM, Ji Y, Gottlieb W, Depinet T, Wandstrat AE, Cassidy SB, Driscoll DJ, Rogan PK, Schwartz S, Nicholls RD 1999. Chromosome breakage in the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes involves recombination between large, transcribed repeats at proximal and distal breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet 65: 370–386 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
