A decision analysis of amputation versus reconstruction for severe open tibial fracture from the physician and patient perspectives
- PMID: 20842003
- PMCID: PMC4382673
- DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181cbfcce
A decision analysis of amputation versus reconstruction for severe open tibial fracture from the physician and patient perspectives
Abstract
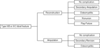
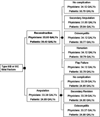
Although reconstruction is often the primary choice of surgeons after an open tibial fracture, there is no evidence to support the long-term effectiveness of flap reconstruction over below-knee amputation. The aim of this study was to perform a decision analysis to evaluate treatment preferences for type IIIB and IIIC tibial fractures. Reconstructive microsurgeons, physical medicine physicians, and patients with lower extremity trauma completed a Web-based standard gamble utility survey to generate quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). Physicians assigned quite high utility values, and there was a slight preference for reconstruction over amputation, with a gain of only 0.55 QALY. Patients assigned significantly lower utility values and also favored reconstruction over amputation, but with a larger gain of 5.54 QALYs. The disparate utilities assigned by the physicians and the patients highlight the necessity of realistic discussion of outcomes, regardless of the management methods.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A qualitative analysis of the decision-making process for patients with severe lower leg trauma.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010 Dec;126(6):2019-2029. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181f4449e. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010. PMID: 20697318 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes after high-energy open tibial fractures: Is a salvaged limb superior to prosthesis in terms of physical function and quality of life?Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019 May;29(4):899-906. doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02382-x. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019. PMID: 30756177
-
[Amputation or reconstruction of IIIB and IIIC open tibial fracture. Decision criteria in the acute phase and late functional outcome].Unfallchirurg. 1998 May;101(5):360-9. doi: 10.1007/s001130050281. Unfallchirurg. 1998. PMID: 9629048 German.
-
Treatment of grade IIIB and grade IIIC open tibial fractures.Orthop Clin North Am. 1994 Oct;25(4):561-71. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994. PMID: 8090470 Review.
-
Ganga hospital open injury score in management of open injuries.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015 Feb;41(1):3-15. doi: 10.1007/s00068-014-0465-9. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015. PMID: 26038161 Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-cultural variation in preference for replantation or revision amputation: Societal and surgeon views.Injury. 2016 Apr;47(4):818-23. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Injury. 2016. PMID: 26961436 Free PMC article.
-
A cost-utility analysis of amputation versus salvage for Gustilo type IIIB and IIIC open tibial fractures.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009 Dec;124(6):1965-1973. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181bcf156. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009. PMID: 19952652 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Health State Utility Values in the Plastic Surgery Literature.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Nov 29;9(11):e3944. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003944. eCollection 2021 Nov. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021. PMID: 34849317 Free PMC article.
-
Limb salvage versus primary amputation in Gustilo-Anderson IIIB and IIIC tibial fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Aug;143(8):4961-4976. doi: 10.1007/s00402-023-04804-2. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 36781435
-
Decision analysis in plastic surgery: a primer.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010 Oct;126(4):1373-1380. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181ead10a. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010. PMID: 20555298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Court-Brown CM, Rimmer S, Prakash U, McQueen MM. The epidemiology of open long bone fractures. Injury. 1998;29(7):529–534. - PubMed
-
- Gustilo RB, Mendoza RM, Williams DN. Problems in the management of type III (severe) open fractures: a new classification of type III open fractures. J Trauma. 1984:2442–2446. - PubMed
-
- Parrett BM, Matros E, Pribaz JJ, Orgill DP. Lower extremity trauma: trends in the management of soft-tissue reconstruction of open tibia-fibula fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(4):1315–1322. - PubMed
-
- Meyer M, Evans J. Joint orthopaedic and plastic surgery management of types III and IV lower limb injuries. Br J Plast Surg. 1990;43(6):692–694. - PubMed
-
- Naique SB, Pearse M, Nanchahal J. Management of severe open tibial fractures: the need for combined orthopaedic and plastic surgical treatment in specialist centres. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(3):351–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

