MicroRNA binding site polymorphisms as biomarkers of cancer risk
- PMID: 20843204
- PMCID: PMC3832135
- DOI: 10.1586/erm.10.59
MicroRNA binding site polymorphisms as biomarkers of cancer risk
Abstract
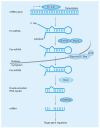
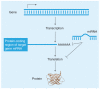
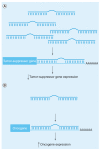
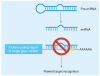
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are well established as global gene regulators and thus, slight alterations in miRNA levels as well as their ability to regulate their targets may cause important cellular changes leading to cancer risk. 3´ untranslated region (UTR) miRNA binding site single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have added another layer of possible genetic variation involved in the complex process of oncogenesis. Identifying these key genetically inherited effectors of miRNA functioning has improved our understanding of the complexity of disease. Interest in the field has grown rapidly in only the last 5 years, with several studies reporting on the role of 3´UTR binding site SNPs as genetic markers of increased cancer susceptibility, as well as biomarkers of cancer type, outcome and response to therapy. Currently, there are numerous known miRNA binding site SNPs associated with multiple cancer subtypes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA binding-site polymorphisms as potential biomarkers of cancer risk.Mol Diagn Ther. 2010 Dec 1;14(6):335-42. doi: 10.1007/BF03256390. Mol Diagn Ther. 2010. PMID: 21275451 Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in cancer susceptibility.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:591931. doi: 10.1155/2013/591931. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23586049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic polymorphisms and microRNAs: new direction in molecular epidemiology of solid cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Jan;16(1):8-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01359.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21692980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphisms in lipid metabolism related miRNA binding sites and risk of metabolic syndrome.Gene. 2013 Oct 10;528(2):132-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23911300
-
Impact of Genetic Variation in MicroRNA-binding Site on Susceptibility to Colorectal Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2016 Jul;36(7):3353-61. Anticancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27354594
Cited by
-
Key principles of miRNA involvement in human diseases.Discoveries (Craiova). 2014 Oct-Dec;2(4):e34. doi: 10.15190/d.2014.26. Discoveries (Craiova). 2014. PMID: 26317116 Free PMC article.
-
A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in HPGD Gene Is Associated with Prostate Cancer Risk.J Cancer. 2017 Oct 24;8(19):4083-4086. doi: 10.7150/jca.22025. eCollection 2017. J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29187884 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1 and TGF-βR1 variants are associated with clinical outcomes in smoking-related head and neck cancer patients treated with chemoradiation through modulating microRNA-mediated regulation.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Mar 30;73(5):85. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03672-y. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38554185 Free PMC article.
-
A miR-SNP biomarker linked to an increased lung cancer survival by miRNA-mediated down-regulation of FZD4 expression and Wnt signaling.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 22;7(1):9029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09604-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28831115 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of microRNA involvement in human cancers.Chin J Cancer. 2011 Nov;30(11):739-48. doi: 10.5732/cjc.011.10243. Chin J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22035854 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
-
Chen K, Song F, Calin GA, Wei Q, Hao X, Zhang W. Polymorphisms in microRNA targets: a gold mine for molecular epidemiology. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(7):1306–1311. • miRNAs are a new and large class of small, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by sequence-specific binding to target mRNAs.
-
-
- Medina PP, Slack FJ. MicroRNAs and cancer: an overview. Cell Cycle. 2008;7(16):2485–2492. - PubMed
-
- Chang TC, Mendell JT. MicroRNAs in vertebrate physiology and human disease. Annu. Rev. Genomics. Hum. Genet. 2007;8:215–239. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: the microRNA sequence database. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006;342:129–138. - PubMed
Websites
-
- miRBase http://microrna.sanger.ac.uk.
-
- American Cancer Society www.cancer.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
