Determinants and prognostic implications of cardiac troponin T measured by a sensitive assay in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 20843304
- PMCID: PMC2946276
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-9-52
Determinants and prognostic implications of cardiac troponin T measured by a sensitive assay in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: The cardiac troponins are biomarkers used for diagnosis of myocardial injury. They are also powerful prognostic markers in many diseases and settings. Recently introduced high-sensitivity assays indicate that chronic cardiac troponin elevations are common in response to cardiovascular (CV) morbidity. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) confers a high risk of CV disease, but little is known about chronic cardiac troponin elevations in diabetic subjects. Accordingly, we aimed to understand the prevalence, determinants, and prognostic implications of cardiac troponin T (cTnT) elevations measured with a high-sensitivity assay in patients with T2DM.
Methods: cTnT was measured in stored, frozen serum samples from 124 subjects enrolled in the Asker and Bærum Cardiovascular Diabetes trial at baseline and at 2-year follow-up, if available (96 samples available). Results were analyzed in relation to baseline variables, hospitalizations, and group assignment (multifactorial intensive versus conventional diabetes care for lowering CV risk).
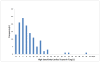
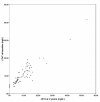
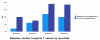
Results: One-hundred thirteen (90%) had detectable cTnT at baseline and of those, 22 (18% of the total population) subjects had values above the 99th percentile for healthy controls (13.5 ng/L). Levels at baseline were associated with conventional CV risk factors (age, renal function, gender). There was a strong correlation between cTnT levels at the two time-points (r=0.92, p>0.001). Risk for hospitalizations during follow-up increased step-wise by quartiles of hscTnT measured at baseline (p=0.058).
Conclusions: Elevations of cTnT above the 99th percentile measured by a highly sensitive assay were encountered frequently in a population of T2DM patients. cTnT levels appeared to be stable over time and associated with conventional CV risk factors. Although a clear trend was present, no statistically robust associations with adverse outcomes could be found.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive value of cardiac troponin T and I in hemodialysis patients.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2012 Sep;23(5):939-45. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.100868. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2012. PMID: 22982904
-
High-sensitive cardiac troponin T and its relations to cardiovascular risk factors, morbidity, and mortality in elderly men.Am Heart J. 2013 Sep;166(3):541-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Am Heart J. 2013. PMID: 24016505
-
A sensitive cardiac troponin T assay in stable coronary artery disease.N Engl J Med. 2009 Dec 24;361(26):2538-47. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805299. Epub 2009 Nov 25. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19940289 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Troponins: Contemporary Biological Data and New Methods of Determination.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2021 Jun 3;17:299-316. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S300002. eCollection 2021. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2021. PMID: 34113117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and significance of detectable troponins as measured by highly sensitive assays in the general population.Coron Artery Dis. 2013 Dec;24(8):705-9. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000048. Coron Artery Dis. 2013. PMID: 24201087 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics and prognostic implications of diabetes and myocardial injury in patients admitted to the emergency room.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Aug 30;21(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02220-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34461832 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of high-sensitivity troponin-I for future adverse cardiovascular outcome in stable patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Mar 25;13:63. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-13-63. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 24661773 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of High-Sensitivity Troponin in Predicting Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 May 11;17(5):e83925. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83925. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40502917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical review: Screening for coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 May;97(5):1434-42. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2122. Epub 2012 Mar 14. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22419711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Familial history of heart disease and increased risk for elevated troponin in apparently healthy individuals.Clin Cardiol. 2019 Aug;42(8):760-767. doi: 10.1002/clc.23214. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Clin Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31175686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selvin E, Marinopoulos S, Berkenblit G, Rami T, Brancati FL, Powe NR, Golden SH. Meta-analysis: glycosylated hemoglobin and cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141:421–431. - PubMed
-
- Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, Hadden D, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000;321:405–412. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7258.405. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

