Klotho interferes with a novel FGF-signalling pathway and insulin/Igf-like signalling to improve longevity and stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 20844315
- PMCID: PMC2984606
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100195
Klotho interferes with a novel FGF-signalling pathway and insulin/Igf-like signalling to improve longevity and stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
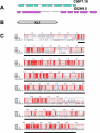
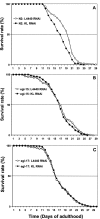
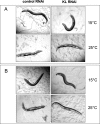
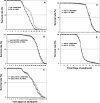
Klotho exerts anti-aging properties in mammals in two different ways. While membrane-bound Klotho, which is primarily expressed in the kidney, acts as an obligate co-receptor of FGF23 to regulate phosphate homeostasis, secreted Klotho, resulting from the shedding of the KL1-KL2 ectodomain into the bloodstream, inhibits Insulin/IGF1 signalling. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, we investigated the biological role of Klotho in Caenorhabditis elegans. Two redundant homologues of the klotho gene exist in C. elegans and encode predicted proteins homologous to the glucosidase-like KL1 domain of mammalian Klotho. We have used a genetic approach to investigate the functional activity of Klotho in C. elegans. Here, we report that whereas Klotho requires EGL-15 (FGFR) and EGL-17 to promote longevity and oxidative stress resistance, it is not involved in the regulation of fluid homeostasis, controlled by LET-756. Besides revealing a new post-developmental role for EGL-17, our data suggest that the KL1 form of Klotho is involved in FGF23-independent FGF signalling. We also report a genetic interaction between Klotho and the DAF-2 (Ins/IGF1R)/DAF-16 (FOXO) pathway. While the regulation of longevity requires functional DAF-2/DAF-16 signalling, the control of oxidative stress resistance involves a DAF-2- independent, DAF-16-dependent pathway, suggesting that Klotho may target either DAF-2 or DAF-16, depending of environmental conditions. Thus, the predictive KL1 form of Klotho appears to crosstalk with both FGF and Insulin/IGF1/FOXO pathways to exert anti-aging properties in C. elegans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures

Comment in
-
CeKlotho opens a new road for investigation in worm aging.Aging (Albany NY). 2010 Sep;2(9):539-40. doi: 10.18632/aging.100198. Aging (Albany NY). 2010. PMID: 20844313 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Triiodothyronine (T3) enhances lifespan and protects against oxidative stress via activation of Klotho in Caenorhabditis elegans.Biogerontology. 2021 Aug;22(4):397-413. doi: 10.1007/s10522-021-09923-0. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Biogerontology. 2021. PMID: 33851304
-
The DAF-16 FOXO transcription factor regulates natc-1 to modulate stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans, linking insulin/IGF-1 signaling to protein N-terminal acetylation.PLoS Genet. 2014 Oct 16;10(10):e1004703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004703. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25330323 Free PMC article.
-
The GATA transcription factor egl-27 delays aging by promoting stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(12):e1003108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003108. Epub 2012 Dec 13. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23271974 Free PMC article.
-
Klotho.Pflugers Arch. 2010 Jan;459(2):333-43. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0722-7. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 19730882 Review.
-
Recent aging research in Caenorhabditis elegans.Exp Gerontol. 2006 Jun;41(6):557-63. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2006.02.008. Epub 2006 Apr 3. Exp Gerontol. 2006. PMID: 16584861 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell Survival, Death, and Proliferation in Senescent and Cancer Cells: the Role of (Poly)phenols.Adv Nutr. 2023 Sep;14(5):1111-1130. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.05.014. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Adv Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37271484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longevity factor klotho and chronic psychological stress.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Jun 16;5(6):e585. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.81. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26080320 Free PMC article.
-
CeKlotho opens a new road for investigation in worm aging.Aging (Albany NY). 2010 Sep;2(9):539-40. doi: 10.18632/aging.100198. Aging (Albany NY). 2010. PMID: 20844313 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
KLOTHO heterozygosity attenuates APOE4-related amyloid burden in preclinical AD.Neurology. 2019 Apr 16;92(16):e1878-e1889. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007323. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Neurology. 2019. PMID: 30867273 Free PMC article.
-
In active acromegaly, IGF1 bioactivity is related to soluble Klotho levels and quality of life.Endocr Connect. 2014 Apr 15;3(2):85-92. doi: 10.1530/EC-14-0028. Print 2014. Endocr Connect. 2014. PMID: 24692508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Kawaguchi H, Suga T, Utsugi T, Ohyama Y, Kurabayashi M, Kaname T, Kume E, Iwasaki H, Iida A, Shiraki-Iida T, Nishikawa S, Nagai R, Nabeshima YI. Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resemblingageing. Nature. 1997;390:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Arking DE, Atzmon G, Arking A, Barzilai N, Dietz HC. Association between a functionalvariant of the KLOTHO gene and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, bloodpressure, stroke, and longevity. Circ Res. 2005;96:412–418. - PubMed
-
- Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Shiraki-Iida T, Nagai R, Kuro-o M, Nabeshima Y. Identification of the human klotho gene and its two transcripts encodingmembrane and secreted klotho protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;242:626–630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

