In vivo imaging of labelled endogenous β-actin mRNA during nucleocytoplasmic transport
- PMID: 20844488
- PMCID: PMC3005609
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09438
In vivo imaging of labelled endogenous β-actin mRNA during nucleocytoplasmic transport
Abstract
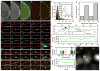
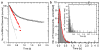
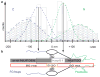
Export of messenger RNA occurs via nuclear pores, which are large nanomachines with diameters of roughly 120 nm that are the only link between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Hence, mRNA export occurs over distances smaller than the optical resolution of conventional light microscopes. There is extensive knowledge on the physical structure and composition of the nuclear pore complex, but transport selectivity and the dynamics of mRNA export at nuclear pores remain unknown. Here we developed a super-registration approach using fluorescence microscopy that can overcome the current limitations of co-localization by means of measuring intermolecular distances of chromatically different fluorescent molecules with nanometre precision. With this method we achieve 20-ms time-precision and at least 26-nm spatial precision, enabling the capture of highly transient interactions in living cells. Using this approach we were able to spatially resolve the kinetics of mRNA transport in mammalian cells and present a three-step model consisting of docking (80 ms), transport (5-20 ms) and release (80 ms), totalling 180 ± 10 ms. Notably, the translocation through the channel was not the rate-limiting step, mRNAs can move bi-directionally in the pore complex and not all pores are equally active.
Figures
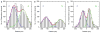
References
-
- Stoffler D, et al. Cryo-electron tomography provides novel insights into nuclear pore architecture: Implications for nucleocytoplasmic transport. J Mol Biol. 2003;328 (1):119–130. - PubMed
-
- Kiseleva E, Goldberg MW, Allen TD, Akey CW. Active nuclear pore complexes in Chironomus: visualization of transporter configurations related to mRNP export. Journal of Cell Science. 1998;111:223–236. - PubMed
-
- Beck M, et al. Nuclear pore complex structure and dynamics revealed by cryoelectron tomography. Science. 2004;306 (5700):1387–1390. - PubMed
-
- Frey S, Gorlich D. A saturated FG-repeat hydrogel can reproduce the permeability properties of nuclear pore complexes. Cell. 2007;130 (3):512–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

