Chromatin landscape dictates HSF binding to target DNA elements
- PMID: 20844575
- PMCID: PMC2936546
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001114
Chromatin landscape dictates HSF binding to target DNA elements
Abstract
Sequence-specific transcription factors (TFs) are critical for specifying patterns and levels of gene expression, but target DNA elements are not sufficient to specify TF binding in vivo. In eukaryotes, the binding of a TF is in competition with a constellation of other proteins, including histones, which package DNA into nucleosomes. We used the ChIP-seq assay to examine the genome-wide distribution of Drosophila Heat Shock Factor (HSF), a TF whose binding activity is mediated by heat shock-induced trimerization. HSF binds to 464 sites after heat shock, the vast majority of which contain HSF Sequence-binding Elements (HSEs). HSF-bound sequence motifs represent only a small fraction of the total HSEs present in the genome. ModENCODE ChIP-chip datasets, generated during non-heat shock conditions, were used to show that inducibly bound HSE motifs are associated with histone acetylation, H3K4 trimethylation, RNA Polymerase II, and coactivators, compared to HSE motifs that remain HSF-free. Furthermore, directly changing the chromatin landscape, from an inactive to an active state, permits inducible HSF binding. There is a strong correlation of bound HSEs to active chromatin marks present prior to induced HSF binding, indicating that an HSE's residence in "active" chromatin is a primary determinant of whether HSF can bind following heat shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
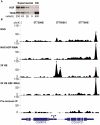
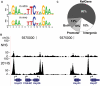
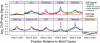
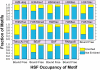
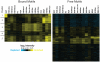
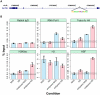
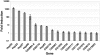
References
-
- Wei CL, Wu Q, Vega VB, Chiu KP, Ng P, et al. A global map of p53 transcription-factor binding sites in the human genome. Cell. 2006;124:207–219. - PubMed
-
- Yang A, Zhu Z, Kapranov P, McKeon F, Church GM, et al. Relationships between p63 binding, DNA sequence, transcription activity, and biological function in human cells. Mol Cell. 2006;24:593–602. - PubMed
-
- Biggin MD, McGinnis W. Regulation of segmentation and segmental identity by Drosophila homeoproteins: The role of DNA binding in functional activity and specificity. Development. 1997;124:4425–4433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

