Role for PKC δ in Fenretinide-Mediated Apoptosis in Lymphoid Leukemia Cells
- PMID: 20844597
- PMCID: PMC2938797
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/584657
Role for PKC δ in Fenretinide-Mediated Apoptosis in Lymphoid Leukemia Cells
Abstract
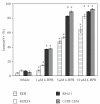
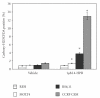
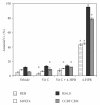
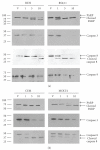
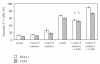
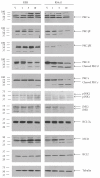
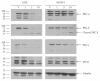
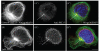
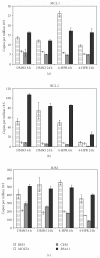
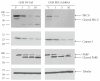
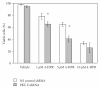
The synthetic Vitamin A analog fenretinide is a promising chemotherapeutic agent. In the current paper, the role of PKC δ was examined in fenretinide-induced apoptosis in lymphoid leukemia cells. Levels of proapoptotic cleaved PKC δ positively correlated with drug sensitivity. Fenretinide promoted reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. The antioxidant Vitamin C prevented fenretinide-induced PKC δ cleavage and protected cells from fenretinide. Suppression of PKC δ expression by shRNA sensitized cells to fenretinide-induced apoptosis possibly by a mechanism involving ROS production. A previous study demonstrated that fenretinide promotes degradation of antiapoptotic MCL-1 in ALL cells via JNK. Now we have found that fenretinide-induced MCL-1 degradation may involve PKC δ as cleavage of the kinase correlated with loss of MCL-1 even in cells when JNK was not activated. These results suggest that PKC δ may play a complex role in fenretinide-induced apoptosis and may be targeted in antileukemia strategies that utilize fenretinide.
Figures
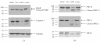


Similar articles
-
PLAB induction in fenretinide-induced apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells occurs via a ROS-dependent mechanism involving ER stress and JNK activation.Carcinogenesis. 2009 May;30(5):824-31. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp067. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Carcinogenesis. 2009. PMID: 19325135
-
Mechanism of synergy of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide and ABT-737 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines: Mcl-1 inactivation.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008 Apr 16;100(8):580-95. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn076. Epub 2008 Apr 8. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008. PMID: 18398104
-
Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Synergism of Fenretinide and Romidepsin in Preclinical Models of T-cell Lymphoid Malignancies.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Apr;16(4):649-661. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0749. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28119491
-
Mechanism of fenretinide (4-HPR)-induced cell death.Apoptosis. 2001 Oct;6(5):377-88. doi: 10.1023/a:1011342220621. Apoptosis. 2001. PMID: 11483862 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of fenretinide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Dec;1028:81-9. doi: 10.1196/annals.1322.009. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15650234 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of ellagic acid in regulation of apoptosis by modulating novel and atypical PKC in lymphoma bearing mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Aug 15;15:281. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0810-5. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26276710 Free PMC article.
-
Atg7 suppression enhances chemotherapeutic agent sensitivity and overcomes stroma-mediated chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia.Blood. 2016 Sep 1;128(9):1260-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-692244. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27268264 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydroceramide accumulation and reactive oxygen species are distinct and nonessential events in 4-HPR-mediated leukemia cell death.Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;90(2):209-23. doi: 10.1139/o2012-001. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22428532 Free PMC article.
-
MEK inhibition enhances ABT-737-induced leukemia cell apoptosis via prevention of ERK-activated MCL-1 induction and modulation of MCL-1/BIM complex.Leukemia. 2012 Apr;26(4):778-87. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.287. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Leukemia. 2012. Retraction in: Leukemia. 2024 Sep;38(9):2072. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02339-y. PMID: 22064351 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Phosphorylation of GSK3α/β correlates with activation of AKT and is prognostic for poor overall survival in acute myeloid leukemia patients.BBA Clin. 2015 Jul 23;4:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2015.07.001. eCollection 2015 Dec. BBA Clin. 2015. PMID: 26674329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corazzari M, Lovat PE, Oliverio S, et al. Fenretinide: a p53-independent way to kill cancer cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2005;331(3):810–815. - PubMed
-
- Lotan R. Retinoids and apoptosis: implications for cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1995;87(22):1655–1657. - PubMed
-
- Maurer BJ, Melton L, Billups C, Cabot MC, Reynolds CP. Synergistic cytotoxicity in solid tumor cell lines between N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide and modulators of ceramide metabolism. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2000;92(23):1897–1909. - PubMed
-
- Sun S-Y, Li W, Yue P, Lippman SM, Hong WK, Lotan R. Mediation of N-(4-hydoxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells by different mechanisms. Cancer Research. 1999;59(10):2493–2498. - PubMed
-
- O’Donnell PH, Guo W-X, Reynolds CP, Maurer BJ. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide increases ceramide and is cytotoxic to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines, but not to non-malignant lymphocytes. Leukemia. 2002;16(5):902–910. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

