Role for PKC δ in Fenretinide-Mediated Apoptosis in Lymphoid Leukemia Cells
- PMID: 20844597
- PMCID: PMC2938797
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/584657
Role for PKC δ in Fenretinide-Mediated Apoptosis in Lymphoid Leukemia Cells
Abstract
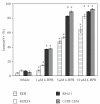
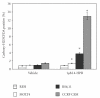
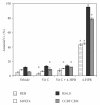
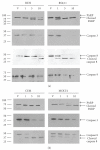
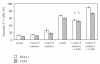
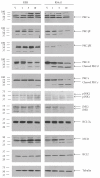
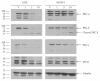
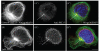
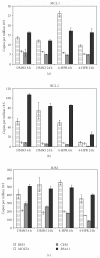
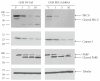
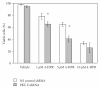
The synthetic Vitamin A analog fenretinide is a promising chemotherapeutic agent. In the current paper, the role of PKC δ was examined in fenretinide-induced apoptosis in lymphoid leukemia cells. Levels of proapoptotic cleaved PKC δ positively correlated with drug sensitivity. Fenretinide promoted reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. The antioxidant Vitamin C prevented fenretinide-induced PKC δ cleavage and protected cells from fenretinide. Suppression of PKC δ expression by shRNA sensitized cells to fenretinide-induced apoptosis possibly by a mechanism involving ROS production. A previous study demonstrated that fenretinide promotes degradation of antiapoptotic MCL-1 in ALL cells via JNK. Now we have found that fenretinide-induced MCL-1 degradation may involve PKC δ as cleavage of the kinase correlated with loss of MCL-1 even in cells when JNK was not activated. These results suggest that PKC δ may play a complex role in fenretinide-induced apoptosis and may be targeted in antileukemia strategies that utilize fenretinide.
Figures
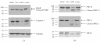


References
-
- Corazzari M, Lovat PE, Oliverio S, et al. Fenretinide: a p53-independent way to kill cancer cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2005;331(3):810–815. - PubMed
-
- Lotan R. Retinoids and apoptosis: implications for cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1995;87(22):1655–1657. - PubMed
-
- Maurer BJ, Melton L, Billups C, Cabot MC, Reynolds CP. Synergistic cytotoxicity in solid tumor cell lines between N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide and modulators of ceramide metabolism. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2000;92(23):1897–1909. - PubMed
-
- Sun S-Y, Li W, Yue P, Lippman SM, Hong WK, Lotan R. Mediation of N-(4-hydoxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells by different mechanisms. Cancer Research. 1999;59(10):2493–2498. - PubMed
-
- O’Donnell PH, Guo W-X, Reynolds CP, Maurer BJ. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide increases ceramide and is cytotoxic to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines, but not to non-malignant lymphocytes. Leukemia. 2002;16(5):902–910. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

