Spontaneously Resolving Periocular Erythema and Ciliary Madarosis Following Intra-arterial Chemotherapy for Retinoblastoma
- PMID: 20844675
- PMCID: PMC2934711
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-9233.65492
Spontaneously Resolving Periocular Erythema and Ciliary Madarosis Following Intra-arterial Chemotherapy for Retinoblastoma
Abstract
Purpose and design: To describe an unusual clinical finding seen in children undergoing intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma.
Materials and methods: A retrospective review of 69 eyes of 63 patients receiving intra-arterial chemotherapy over a 3-year period. Charts and photographs of 69 consecutive cases were reviewed, and data were collected on patients with clinical evidence of a hyperemic cutaneous periocular abnormality following the procedure.
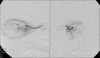
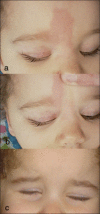
Results: A blanching erythematous and edematous patch was noted in the periocular region in 16% (11 of 69) of the children who received intraarterial chemotherapy. The plaque extended into the region of the supertrochlear and medial marginal artery distribution on the ipsilateral side of the intra-arterial chemotherapy. All patches of erythema spontaneously resolved within 3 months following completion of the intra-arterial chemotherapy.
Conclusion: Periocular erythema and swelling is a self-limited clinical finding associated with intra-arterial chemotherapy in a small number of patients.
Keywords: Cancer; Eye; Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy; Melphalan; Retinoblastoma; Skin; Topotican.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Superselective intra-arterial chemotherapy in the primary management of advanced intra-ocular retinoblastoma: first 4-year experience from a single institution in Turkey.Acta Ophthalmol. 2016 Nov;94(7):e644-e651. doi: 10.1111/aos.13077. Epub 2016 May 23. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27214798
-
Intra-arterial chemotherapy is more effective than sequential periocular and intravenous chemotherapy as salvage treatment for relapsed retinoblastoma.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013 May;60(5):766-70. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24356. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23024125
-
Rescue intra-arterial chemotherapy following retinoblastoma recurrence after initial intra-arterial chemotherapy.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2015 Jun;38(6):542-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 May 14. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2015. PMID: 25982423
-
Ciliary Madarosis Secondary to Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy for Retinoblastoma Treatment.Skin Appendage Disord. 2024 Jun;10(3):167-171. doi: 10.1159/000535826. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Skin Appendage Disord. 2024. PMID: 38835713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted retinoblastoma management: when to use intravenous, intra-arterial, periocular, and intravitreal chemotherapy.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2014 Sep;25(5):374-85. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000091. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25014750 Review.
Cited by
-
Validating a nonhuman primate model of super-selective intraophthalmic artery chemotherapy: comparing ophthalmic artery diameters.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Nov 27;53(12):7791-4. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10605. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 23111611 Free PMC article.
-
Madarosis: a marker of many maladies.Int J Trichology. 2012 Jan;4(1):3-18. doi: 10.4103/0974-7753.96079. Int J Trichology. 2012. PMID: 22628984 Free PMC article.
-
Modern treatment of retinoblastoma: A 2020 review.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020 Nov;68(11):2356-2365. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_721_20. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33120616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enucleated eyes after failed intra-arterial infusion of chemotherapy for unilateral retinoblastoma: histopathologic evaluation of vitreous seeding.Clin Ophthalmol. 2011;5:1655-8. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S24318. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Clin Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 22174572 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy (Ophthalmic Artery Chemosurgery) for Group D Retinoblastoma.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 12;11(1):e0146582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146582. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26756643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson DH, Dunkel IJ, Brodie SE, Kim JW, Gobin YP. A phase I/II study of direct intra-arterial (ophthalmic artery) chemotherapy with melphalan for intraocular retinoblastoma initial results. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:1398–404. - PubMed
-
- Abramson DH, Dunkel IJ, Brodie SE, Marr B, Gobin YP. Bilateral superselective ophthalmic artery chemotherapy for bilateral retinoblastoma: Tandem therapy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:370–2. - PubMed
-
- Brodie SE, Pierre Gobin Y, Dunkel IJ, Kim JW, Abramson DH. Persistence of retinal function after selective ophthalmic artery chemotherapy infusion for retinoblastoma. Doc Ophthalmol. 2009;119:13–22. - PubMed
-
- Claudio F, Cacace F, Comella G, Coucourde F, Claudio L, Bevilacqua AM, et al. Intraarterial chemotherapy through carotid transposition in advanced head and neck cancer. Cancer. 1990;65:1465–71. - PubMed
-
- Landau M, Brenner S, Gat A, Klausner JM, Gutman M. Reticulate scleroderma after isolated limb perfusion with melphalan. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:1011–2. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

