NF-κB as a target for oncogenic viruses
- PMID: 20845110
- PMCID: PMC3855473
- DOI: 10.1007/82_2010_108
NF-κB as a target for oncogenic viruses
Abstract
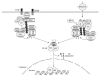
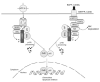
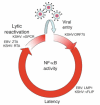
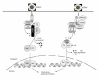
NF-κB is a pivotal transcription factor that controls cell survival and proliferation in diverse physiological processes. The activity of NF-κB is tightly controlled through its cytoplasmic sequestration by specific inhibitors, IκBs. Various cellular stimuli induce the activation of an IκB kinase, which phosphorylates IκBs and triggers their proteasomal degradation, causing nuclear translocation of activated NF-κB. Under normal conditions, the activation of NF-κB occurs transiently, thus ensuring rapid but temporary induction of target genes. Deregulated NF-κB activation contributes to the development of various diseases, including cancers and immunological disorders. Accumulated studies demonstrate that the NF-κB signaling pathway is a target of several human oncogenic viruses, including the human T cell leukemia virus type 1, the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, and the Epstein-Bar virus. These viruses encode specific oncoproteins that target different signaling components of the NF-κB pathway, leading to persistent activation of NF-κB. This chapter will discuss the molecular mechanisms by which NF-κB is activated by the viral oncoproteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Persistent activation of NF-kappaB by the tax transforming protein of HTLV-1: hijacking cellular IkappaB kinases.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 22;18(49):6948-58. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203220. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10602469 Review.
-
The Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Transactivator CIITA Inhibits the Persistent Activation of NF-κB by the Human T Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 Tax-1 Oncoprotein.J Virol. 2016 Jan 20;90(7):3708-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03000-15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26792751 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NF-kappaB by HTLV-I and implications for cell transformation.Oncogene. 2005 Sep 5;24(39):5952-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208969. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16155602 Review.
-
Upregulation of MicroRNA 711 Mediates HIV-1 Vpr Promotion of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency and Induction of Pro-proliferation and Pro-survival Cytokines by Targeting the Notch/NF-κB-Signaling Axis.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00580-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00580-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29976660 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax induction of NF-kappaB involves activation of the IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) and IKKbeta cellular kinases.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Sep;18(9):5157-65. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.9.5157. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9710600 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
KSHV-encoded vCyclin can modulate HIF1α levels to promote DNA replication in hypoxia.Elife. 2021 Jul 19;10:e57436. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57436. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34279223 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Activation Is Essential for Cervical Cell Proliferation and Malignant Transformation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 11;26(6):2493. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062493. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141137 Free PMC article.
-
HBx-induced NF-κB signaling in liver cells is potentially mediated by the ternary complex of HBx with p22-FLIP and NEMO.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57331. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057331. Epub 2013 Mar 4. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23483900 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus and the landscape of secondary genetic alterations in oral cancers.Genome Res. 2019 Jan;29(1):1-17. doi: 10.1101/gr.241141.118. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 30563911 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Zinc finger A20 and NF-κB correlate with high-risk human papillomavirus of squamous cell carcinoma patients.Tumour Biol. 2014 Dec;35(12):11855-60. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2416-9. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25230785
References
-
- Adhikari A, Xu M, Chen ZJ. Ubiquitin-mediated activation of TAK1 and IKK. Oncogene. 2007;26:3214–3226. - PubMed
-
- Ariza ME, Glaser R, Kaumaya PT, Jones C, Williams MV. The EBV-encoded dUTPase activates NF-kappa B through the TLR2 and MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. J Immunol. 2009;182:851–9. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis L, Mesri EA, Nador R, Said JW, Asch AS, Knowles DM, Cesarman E. Establishment and characterization of a primary effusion (body cavity-based) lymphoma cell line (BC-3) harboring Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) in the absence of Epstin-Barr virus. Blood. 1996;88:2648–2654. - PubMed
-
- Babcock GJ, Hochberg D, Thorley-Lawson AD. The expression pattern of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes in vivo is dependent upon the differentiation stage of the infected B cell. Immunity. 2000;13:497–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

