Current event-free survival after sequential tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 20845478
- PMCID: PMC4327987
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.25604
Current event-free survival after sequential tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Background: Imatinib is an effective tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase (CP). Although some patients may fail on therapy with imatinib, effective salvage therapy is available with second-generation TKIs. Current measurement of efficacy for each therapy is judged by its individual impact on overall survival and event-free survival (EFS).
Methods: In total, 586 patients with CML in CP who received imatinib were included in this analysis in 2 cohorts: imatinib as front-line therapy (n = 281) or after failure on interferon-α (IFN-α) (n = 305). By accounting for successful salvage treatment (ie, regain of complete cytogenetic response), the current EFS (CEFS) rate was calculated to obtain a more accurate impression of the outcome of patients with CML who received treatment with sequential TKIs.
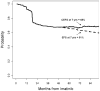
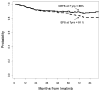
Results: For patients who received imatinib after failing on IFN-α, the 7-year EFS rate was 61%, whereas the CEFS rate was 69%. The 7-year EFS rate for patients who received imatinib as initial therapy was 81% compared with a 7-year CEFS rate of 88%.
Conclusions: CEFS provided a more accurate representation of the outcome of patients with CML in CP. These patients may frequently be treated successfully with subsequent TKIs after experiencing failure on the first TKI.
Copyright © 2010 American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES
Dr. Cortes received research support from Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Wyeth. Dr. Kantarjian received research support from Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Figures
Comment in
-
Second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia: before or after imatinib?Cancer. 2011 Jan 15;117(2):234-7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25600. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21210471 No abstract available.
References
-
- Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, O’Brien S, Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM. The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:164–172. - PubMed
-
- Horner MJ, Ries LAG, Krapcho M, et al., editors. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2006. Bethesda, Md: National Cancer Institute; [Accessed April 2010]. Based on November 2008 SEER data submission; posted to the SEER website 2009: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2006.
-
- Guilhot F, Chastang C, Michallet M, et al. Interferon alfa-2b combined with cytarabine versus interferon alone in chronic myelogenous leukemia. French Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:223–229. - PubMed
-
- Bonifazi F, de Vivo A, Rosti G, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia and interferon-alpha: a study of complete cytogenetic responders. Blood. 2001;98:3074–3081. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

