The calpain inhibitor calpeptin prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 20846163
- PMCID: PMC3026560
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04257.x
The calpain inhibitor calpeptin prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice
Abstract
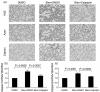
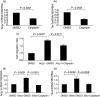
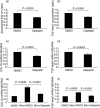
Pulmonary fibrosis is characterized by progressive worsening of pulmonary function leading to a high incidence of death. Currently, however, there has been little progress in therapeutic strategies for pulmonary fibrosis. There have been several reports on cytokines being associated with lung fibrosis, including interleukin (IL)-6 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1. We reported recently that two substances (ATRA and thalidomide) have preventive effects on pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting IL-6-dependent proliferation and TGF-β1-dependent transdifferentiation of lung fibroblasts. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder, and its pathogenesis is also characterized by an association with several cytokines. It has been reported that calpain, a calcium-dependent intracellular cysteine protease, plays an important role in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. In this study, we examined the preventive effect of Calpeptin, a calpain inhibitor, on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. We performed histological examinations and quantitative measurements of IL-6, TGF-β1, collagen type Iα1 and angiopoietin-1 in bleomycin-treated mouse lung tissues with or without the administration of Calpeptin. Calpeptin histologically ameliorated bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Calpeptin decreased the expression of IL-6, TGF-β1, angiopoietin-1 and collagen type Iα1 mRNA in mouse lung tissues. In vitro studies disclosed that Calpeptin reduced (i) production of IL-6, TGF-β1, angiopoietin-1 and collagen synthesis from lung fibroblasts; and (ii) both IL-6-dependent proliferation and angiopoietin-1-dependent migration of the cells, which could be the mechanism underlying the preventive effect of Calpeptin on pulmonary fibrosis. These data suggest the clinical use of Calpeptin for the prevention of pulmonary fibrosis.
© 2010 Authors. Clinical and Experimental Immunology © 2010 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
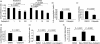
Similar articles
-
Thalidomide prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 1;179(1):708-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.708. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17579094
-
All-trans-retinoic acid prevents radiation- or bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 Dec 15;174(12):1352-60. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200606-862OC. Epub 2006 Oct 5. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 17023731
-
Calpain inhibition attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via switching the development of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;391(7):695-704. doi: 10.1007/s00210-018-1499-z. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29666896 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary fibrosis and type-17 immunity.Respir Investig. 2023 Sep;61(5):553-562. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2023.05.005. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Respir Investig. 2023. PMID: 37356133 Review.
-
Pulmonary toxicants and fibrosis: innate and adaptive immune mechanisms.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 15;409:115272. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115272. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33031836 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic use of calpeptin in COVID-19 infection.Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Oct 28;136(20):1439-1447. doi: 10.1042/CS20220638. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36268783 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Calpain in Pathogenesis of Human Disease Processes.J Nat Sci. 2016;2(9):e218. J Nat Sci. 2016. PMID: 27747292 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain mediates pulmonary vascular remodeling in rodent models of pulmonary hypertension, and its inhibition attenuates pathologic features of disease.J Clin Invest. 2011 Nov;121(11):4548-66. doi: 10.1172/JCI57734. Epub 2011 Oct 17. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 22005303 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid cell-specific deletion of Capns1 prevents macrophage polarization toward the M1 phenotype and reduces interstitial lung disease in the bleomycin model of systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Jun 21;24(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02833-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35729674 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide protects against TGF-β1-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating FAK/calpain signaling.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Dec;18(6):4781-4789. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8127. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31777561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coultas DB, Zumwalt RE, Black WC, Sobonya RE. The epidemiology of interstitial lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;150:967–72. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. - PubMed
-
- Gross TJ, Hunninghake GW. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:517–25. - PubMed
-
- Mason RJ, Schwarz MI, Hunninghake GW, Musson RA. NHLBI Workshop Summary. Pharmacological therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Past, present, and future. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:1771–7. - PubMed
-
- Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J. The calpain system. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:731–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

