Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid induces apoptosis and sub-G1 arrest of 320 HSR colon cancer cells
- PMID: 20846458
- PMCID: PMC2949718
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-76
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid induces apoptosis and sub-G1 arrest of 320 HSR colon cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Histone deacetylases and histone acetyl transferases covalently modify histone proteins, consequentially altering chromatin architecture and gene expression.
Methods: The effects of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, a HDAC inhibitor, on 320 HSR colon cells were assessed in 320 HSR colon cancer cells.
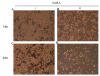
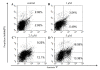
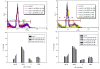
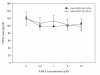
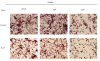
Results: Concentration and time-dependent inhibition of 320 HSR cell proliferation was observed. Treatment of 320 HSR cells with 5 μM SAHA for 72 h significantly inhibited their growth by 50% as compared to that of the control. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis demonstrated significant inhibition of cell cycle progression (sub-G1 arrest) and induction of apoptosis upon various SAHA concentrations after 48 h. In addition, the anti-apoptosis proteins, survivin and Bcl-xL, were significantly inhibited by SAHA after 72 h of treatment. Immunocytochemistry analysis revealed that SAHA-resistant cells were positive for cyclin A (85%), ki-67 (100%), p53 (100%), survivin (100%), and p21 (90%) expression. Furthermore, a significant increase cyclin A-, Ki-67-, p53-, survivin-, and p21-positive cells were noted in SAHA-resistant tumor cells.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated for the first time in 320 HSR colon adenocarcinoma cells that SAHA might be considered as an adjuvant therapy for colon adenocarcinoma.
Figures




References
-
- Kim DH, Kim M, Kwon HJ. Histone deacetylase in carcinogenesis and its inhibitors as anti-cancer agents. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;36:110–119. - PubMed
-
- Truchet I, Jozan S, Baron S, Frongia C, Balaguer P, Richard-Foy H, Valette A. Estrogen and antiestrogen-dependent regulation of breast cancer cell proliferation in multicellular spheroids: Influence of cell microenvironment. Int J Oncol. 2008;32:1033–1039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

