Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect
- PMID: 20846876
- PMCID: PMC2967652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2010.08.002
Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect
Abstract
Because leptin reduces food intake and body weight, the coexistence of elevated leptin levels with obesity is widely interpreted as evidence of 'leptin resistance.' Indeed, obesity promotes a number of cellular processes that attenuate leptin signaling (referred to here as 'cellular leptin resistance') and amplify the extent of weight gain induced by genetic and environmental factors. As commonly used, however, the term 'leptin resistance' embraces a range of phenomena that are distinct in underlying mechanisms and pathophysiological implications. Moreover, the induction of cellular leptin resistance by obesity complicates efforts to distinguish the mechanisms that predispose to weight gain from those that result from it. We suggest a framework for approaching these issues and important avenues for future investigation.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts: RJS receives research support, consults, and is on the speakers’ bureau for Amylin Pharmaceuticals, and is on the speakers’ bureau and scientific advisory board for Novo Nordisk.
Figures
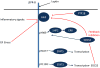
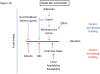


References
-
- Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D, Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature. 2000;404:661–671. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL. The role of leptin in human physiology. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:913–915. - PubMed
-
- Ahima RS, Saper CB, Flier JS, Elmquist JK. Leptin regulation of neuroendocrine systems. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2000;21:263–307. - PubMed
-
- Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, Lallone RL, Burley SK, Friedman JM. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995;269:543–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK057768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK056731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK52431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK052989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK083042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK056731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK078056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

