Human box C/D snoRNAs with miRNA like functions: expanding the range of regulatory RNAs
- PMID: 20846955
- PMCID: PMC3025573
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq776
Human box C/D snoRNAs with miRNA like functions: expanding the range of regulatory RNAs
Abstract
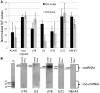
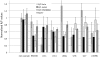
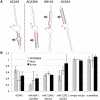
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and microRNAs are two classes of non-protein-coding RNAs with distinct functions in RNA modification or post-transcriptional gene silencing. In this study, we introduce novel insights to RNA-induced gene activity adjustments in human cells by identifying numerous snoRNA-derived molecules with miRNA-like function, including H/ACA box snoRNAs and C/D box snoRNAs. In particular, we demonstrate that several C/D box snoRNAs give rise to gene regulatory RNAs, named sno-miRNAs here. Our data are complementing the increasing number of studies in the field of small RNAs with regulatory functions. In massively deep sequencing of small RNA fractions we identified high copy numbers of sub-sequences from >30 snoRNAs with lengths of ≥18 nt. RNA secondary structure prediction indicated for a majority of candidates a location in predicted stem regions. Experimental analysis revealed efficient gene silencing for 11 box C/D sno-miRNAs, indicating cytoplasmic processing and recruitment to the RNA silencing machinery. Assays in four different human cell lines indicated variations in both the snoRNA levels and their processing to active sno-miRNAs. In addition we show that box D elements are predominantly flanking at least one of the sno-miRNA strands, while the box C element locates within the sequence of the sno-miRNA guide strand.
Figures


References
-
- Filipowicz W, Jaskiewicz L, Kolb FA, Pillai RS. Post-transcriptional gene silencing by siRNAs and miRNAs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005;15:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Meister G, Tuschl T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature. 2004;431:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Seto AG, Kingston RE, Lau NC. The coming of age for Piwi proteins. Mol. Cell. 2007;26:603–609. - PubMed
-
- Aravin AA, Hannon GJ, Brennecke J. The Piwi-piRNA pathway provides an adaptive defense in the transposon arms race. Science. 2007;318:761–764. - PubMed
-
- Aravin AA, Sachidanandam R, Girard A, Fejes-Toth K, Hannon GJ. Developmentally regulated piRNA clusters implicate MILI in transposon control. Science. 2007;316:744–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

