Relating introspective accuracy to individual differences in brain structure
- PMID: 20847276
- PMCID: PMC3173849
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1191883
Relating introspective accuracy to individual differences in brain structure
Erratum in
- Science. 2012 May 11;336(6082):670
Abstract
The ability to introspect about self-performance is key to human subjective experience, but the neuroanatomical basis of this ability is unknown. Such accurate introspection requires discriminating correct decisions from incorrect ones, a capacity that varies substantially across individuals. We dissociated variation in introspective ability from objective performance in a simple perceptual-decision task, allowing us to determine whether this interindividual variability was associated with a distinct neural basis. We show that introspective ability is correlated with gray matter volume in the anterior prefrontal cortex, a region that shows marked evolutionary development in humans. Moreover, interindividual variation in introspective ability is also correlated with white-matter microstructure connected with this area of the prefrontal cortex. Our findings point to a focal neuroanatomical substrate for introspective ability, a substrate distinct from that supporting primary perception.
Figures

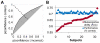
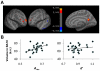
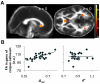
Comment in
-
Neuroscience. Should confidence be trusted?Science. 2010 Sep 17;329(5998):1478-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1195983. Science. 2010. PMID: 20847258 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cleeremans A, Timmermans B, Pasquali A. Consciousness and metarepresentation: A computational sketch. Neural Networks. 2007;20:1032. - PubMed
-
- Metcalfe J. Metacognition: Knowing About Knowing. MIT Press; 1996.
-
- Lau HC. A higher order Bayesian decision theory of consciousness. Prog. Brain Res. 2008;168:35. - PubMed
-
- Kunimoto C, Miller J, Pashler H. Confidence and accuracy of near-threshold discrimination responses. Conscious. Cogn. 2001;10:294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

