Lack of fetuin-A (alpha2-HS-glycoprotein) reduces mammary tumor incidence and prolongs tumor latency via the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway in a mouse model of breast cancer
- PMID: 20847285
- PMCID: PMC2966818
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100177
Lack of fetuin-A (alpha2-HS-glycoprotein) reduces mammary tumor incidence and prolongs tumor latency via the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway in a mouse model of breast cancer
Abstract
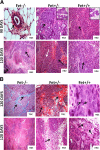
The present analyses were done to define the role of fetuin-A (Fet) in mammary tumorigenesis using the polyoma middle T antigen (PyMT) transgenic mouse model. We crossed Fet-null mice in the C57BL/6 background with PyMT mice in the same background and after a controlled breeding protocol obtained PyMT/Fet+/+, PyMT/Fet+/-, and PyMT/Fet-/- mice that were placed in control and experimental groups. Whereas the control group (PyMT/Fet+/+) formed mammary tumors 90 days after birth, tumor latency was prolonged in the PyMT/Fet-/- and PyMT/Fet+/- mice. The majority of the PyMT/Fet-/- mice were tumor-free at the end of the study, at approximately 40 weeks. The pathology of the mammary tumors in the Fet-null mice showed extensive fibrosis, necrosis, and squamous metaplasia. The preneoplastic mammary tissues of the PyMT/Fet-/- mice showed intense phopho-Smad2/3 staining relative to control tissues, indicating that transforming growth factor-β signaling is enhanced in these tissues in the absence of Fet. Likewise, p19ARF and p53 were highly expressed in tumor tissues of PyMT/Fet-/- mice relative to the controls in the absence of Fet. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway that we previously showed to be activated by Fet, on the other hand, was unaffected by the absence of Fet. The data indicate that Fet is a powerful modulator of breast tumorigenesis in this model system and has the potential to modulate breast cancer progression in humans.
Figures

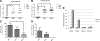




References
-
- Nie Z. Fetuin: its enigmatic property of growth promotion. Am J Physiol. 1992;263:C551–C562. - PubMed
-
- Jahnen-Dechent W, Schinke T, Trindl A, Muller-Esterl W, Sablitzky F, Kaiser S, Blessing M. Cloning and targeted deletion of the mouse fetuin gene. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31496–31503. - PubMed
-
- Kundranda MN, Henderson M, Carter KJ, Gorden L, Binhazim A, Ray S, Baptiste T, Shokrani M, Leite-Browning ML, Jahnen-Dechent W, Matrisian LM, Ochieng J. The serum glycoprotein fetuin-A promotes Lewis lung carcinoma tumorigenesis via adhesive-dependent and adhesive-independent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2005;65:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Swallow CJ, Partridge EA, Macmillan JC, Tajirian T, DiGuglielmo GM, Hay K, Szweras M, Jahnen-Dechent W, Wrana JL, Redston M, Gallinger S, Dennis JW. α2HS-glycoprotein, an antagonist of transforming growth factor β in vivo, inhibits intestinal tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6402–6409. - PubMed
-
- Triffitt JT, Gebauer U, Ashton BA, Owen ME, Reynolds JJ. Origin of plasma α2-HS-glycoprotein and its accumulation in bone. Nature. 1976;262:226–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

