The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids
- PMID: 20847327
- PMCID: PMC4846276
- DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.147405
The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, noncoding RNAs that play an important role in regulating various biological processes through their interaction with cellular messenger RNAs. Extracellular miRNAs in serum, plasma, saliva, and urine have recently been shown to be associated with various pathological conditions including cancer.
Methods: With the goal of assessing the distribution of miRNAs and demonstrating the potential use of miRNAs as biomarkers, we examined the presence of miRNAs in 12 human body fluids and urine samples from women in different stages of pregnancy or patients with different urothelial cancers. Using quantitative PCR, we conducted a global survey of the miRNA distribution in these fluids.
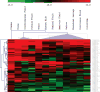
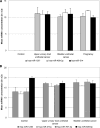
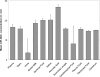
Results: miRNAs were present in all fluids tested and showed distinct compositions in different fluid types. Several of the highly abundant miRNAs in these fluids were common among multiple fluid types, and some of the miRNAs were enriched in specific fluids. We also observed distinct miRNA patterns in the urine samples obtained from individuals with different physiopathological conditions.
Conclusions: MicroRNAs are ubiquitous in all the body fluid types tested. Fluid type-specific miRNAs may have functional roles associated with the surrounding tissues. In addition, the changes in miRNA spectra observed in the urine samples from patients with different urothelial conditions demonstrates the potential for using concentrations of specific miRNAs in body fluids as biomarkers for detecting and monitoring various physiopathological conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Do platform-specific factors explain microRNA profiling disparities?Clin Chem. 2012 Feb;58(2):472-4; author reply 474-5. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2011.175281. Epub 2011 Nov 2. Clin Chem. 2012. PMID: 22048406 No abstract available.
-
The Ubiquitous Existence of MicroRNA in Body Fluids.Clin Chem. 2017 Mar;63(3):784-785. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.267625. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Clin Chem. 2017. PMID: 28082463 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nelson P, Kiriakidou M, Sharma A, Maniataki E, Mourelatos Z. The microRNA world: small is mighty. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28:534–40. - PubMed
-
- Mishima T, Mizuguchi Y, Kawahigashi Y, Takizawa T, Takizawa T. RT-PCR-based analysis of microRNA (miR-1 and −124) expression in mouse CNS. Brain Res. 2007;1131:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Chang J, Nicolas E, Marks D, Sander C, Lerro A, Buendia MA, et al. miR-122, a mammalian liver-specific microRNA, is processed from HCR mRNA and may downregulate the high affinity cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1. RNA Biol. 2004;1:106–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

