Cellular sources and immune functions of interleukin-9
- PMID: 20847745
- PMCID: PMC3828627
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2848
Cellular sources and immune functions of interleukin-9
Abstract
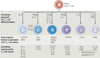
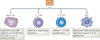
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) has attracted renewed interest owing to the identification of its expression by multiple T helper (T(H)) cell subsets, including T(H)2 cells, T(H)9 cells, T(H)17 cells and regulatory T (T(Reg)) cells. Here, we provide a broad overview of the conditions that are required for cells to produce IL-9 and describe the cellular targets and nature of the immune responses that are induced by IL-9.
Figures

References
-
- Bauer JH, Liu KD, You Y, Lai SY, Goldsmith MA. Heteromerization of the γ chain with the interleukin-9 receptor α subunit leads to STAT activation and prevention of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:9255–9260. - PubMed
-
- Demoulin JB, Van Roost E, Stevens M, Groner B, Renauld JC. Distinct roles for STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5 in differentiation gene induction and apoptosis inhibition by interleukin-9. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:25855–25861. - PubMed
-
- Gessner A, Blum H, Rollinghoff M. Differential regulation of IL-9-expression after infection with Leishmania major in susceptible and resistant mice. Immunobiology. 1993;189:419–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

