Increased serum levels of tumour-associated trypsin inhibitor independently predict a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients
- PMID: 20849596
- PMCID: PMC2946315
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-498
Increased serum levels of tumour-associated trypsin inhibitor independently predict a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients
Abstract
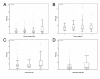
Background: There is an insufficient number of reliable prognostic and response predictive biomarkers in colorectal cancer (CRC) management. In a previous study, we found that high tumour tissue expression of tumour-associated trypsin inhibitor (TATI) correlated with liver metastasis and an impaired prognosis in CRC. The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic validity of serum TATI (s-TATI) in CRC. We further assessed the prognostic value of carcino-embryonic antigen in serum (s-CEA) and the interrelationship between s-TATI and TATI in tissue (t-TATI).
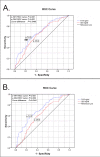
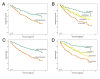
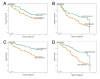
Methods: Using an immunofluorometric assay, s-TATI levels were analysed in 334 preoperatively collected serum samples from patients with CRC. Spearman's Rho and Chi-square test were used for analysis of correlations between s-TATI and clinicopathological parameters, s-CEA and t-TATI. Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox uni- and multivariate regression analysis were used to estimate disease free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) according to quartiles of s-TATI and cut-offs derived from ROC-analysis of s-TATI and s-CEA.
Results: Increased levels of s-TATI were associated with a reduced DFS (HR = 2.00; 95% CI 1.40-2.84, P < 0.001) and OS (HR = 2.40; 95% CI 1.74-3.33, P < 0.001). (HR = 2.89; 95% CI 1.96-4.25). This association remained significant in multivariate analysis. The association for OS remained significant in multivariate analysis (HR = 1.51; 95% CI 1.03-2.22, P = 0.034 for DFS and HR = 1.78; 95% CI 1.25-2.53, P = 0.001 for OS). There was no significant association between s-TATI and t-TATI. The prognostic value of s-CEA was also evident, but somewhat weaker than for s-TATI.
Conclusions: High preoperative s-TATI levels predict a poor prognosis in patients with CRC, and the prognostic value is independent of established prognostic parameters and t-TATI expression. These data suggest that s-TATI might be a useful marker for prognostic stratification in CRC.
Figures
References
-
- Gaber A, Johansson M, Stenman UH, Hotakainen K, Ponten F, Glimelius B, Bjartell A, Jirstrom K, Birgisson H. High expression of tumour-associated trypsin inhibitor correlates with liver metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. British journal of cancer. 2009;100(10):1540–1548. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605047. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gouyer V, Fontaine D, Dumont P, de Wever O, Fontayne-Devaud H, Leteurtre E, Truant S, Delacour D, Drobecq H, Kerckaert JP. et al. Autocrine induction of invasion and metastasis by tumor-associated trypsin inhibitor in human colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008;27(29):4024–4033. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.42. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

