Identification of aneuploidy-tolerating mutations
- PMID: 20850176
- PMCID: PMC2993244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.08.038
Identification of aneuploidy-tolerating mutations
Abstract
Aneuploidy causes a proliferative disadvantage in all normal cells analyzed to date, yet this condition is associated with a disease characterized by unabated proliferative potential, cancer. The mechanisms that allow cancer cells to tolerate the adverse effects of aneuploidy are not known. To probe this question, we identified aneuploid yeast strains with improved proliferative abilities. Their molecular characterization revealed strain-specific genetic alterations as well as mutations shared between different aneuploid strains. Among the latter, a loss-of-function mutation in the gene encoding the deubiquitinating enzyme Ubp6 improves growth rates in four different aneuploid yeast strains by attenuating the changes in intracellular protein composition caused by aneuploidy. Our results demonstrate the existence of aneuploidy-tolerating mutations that improve the fitness of multiple different aneuploidies and highlight the importance of ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation in suppressing the adverse effects of aneuploidy.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

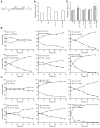
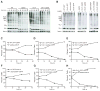
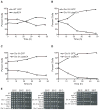
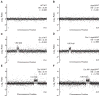
Comment in
-
How to survive aneuploidy.Cell. 2010 Oct 1;143(1):27-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.030. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20887888 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosomal instability: Coping with extra copies.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Nov;10(11):737. doi: 10.1038/nrc2952. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21080579 No abstract available.
References
-
- Albertson DG, Collins C, McCormick F, Gray JW. Chromosome aberrations in solid tumors. Nat Genet. 2003;34:369–376. - PubMed
-
- Chernova TA, Allen KD, Wesoloski LM, Shanks JR, Chernoff YO, Wilkinson KD. Pleiotropic effects of Ubp6 loss on drug sensitivities and yeast prion are due to depletion of the free ubiquitin pool. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:52102–52115. - PubMed
-
- Davies J, Davis BD. Misreading of ribonucleic acid code words induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. The effect of drug concentration. J Biol Chem. 1968;243:3312–3316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

