In vivo multisite oximetry using EPR-NMR coimaging
- PMID: 20850361
- PMCID: PMC2956866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2010.08.011
In vivo multisite oximetry using EPR-NMR coimaging
Abstract
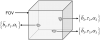
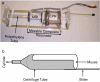
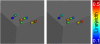
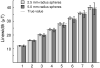
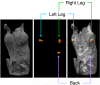
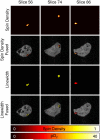
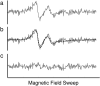
Coimaging employing electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) imaging and MRI is used for rapid in vivo oximetry conducted simultaneously across multiple organs of a mouse. A recently developed hybrid EPR-NMR coimaging instrument is used for both EPR and NMR measurements. Oxygen sensitive particulate EPR probe is implanted in small localized pockets, called sites, across multiple regions of a live mouse. Three dimensional MRI is used to generate anatomic visualization, providing precise locations of implant sites. The pO₂ values, one for every site, are then estimated from EPR measurements. To account for radio frequency (RF) phase inhomogeneities inside a large resonator carrying a lossy sample, a generalization of an existing EPR data model is proposed. Utilization of known spectral lineshape, sparse distribution, and known site locations reduce the EPR data collection by more than an order of magnitude over a conventional spectral-spatial imaging, enhancing the feasibility of in vivo EPR oximetry for clinically relevant models.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Raymond J, Segre D. The effect of oxygen on biochemical networks and the evolution of complex life. Science. 2006;311:1764–1767. - PubMed
-
- Berner R, VandenBrooks J, Ward P. Oxygen and Evolution. Science. 2007;316:557–558. - PubMed
-
- Springett R, Swartz H. Measurement of Oxygen In Vivo: Overview and Perspectives on Methods to Measure Oxygen Within Cells and Tissues. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007;9:1295–1301. - PubMed
-
- Vikram D, Zweier J, Kuppusamy P. Methods for Noninvasive Imaging of Tissue Hypoxia. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007;9:1745–1756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

