Current focusing sharpens local peaks of excitation in cochlear implant stimulation
- PMID: 20850513
- PMCID: PMC2997903
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2010.09.004
Current focusing sharpens local peaks of excitation in cochlear implant stimulation
Abstract
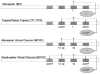
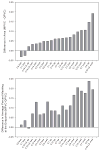
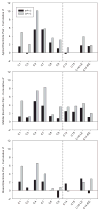
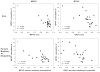
Cochlear implant (CI) users' spectral resolution is limited by the number of implanted electrodes, interactions between the electrodes, and the underlying neural population. Current steering has been proposed to increase the number of spectral channels beyond the number of physical electrodes, however, electric field interactions may limit CI users' access to current-steered virtual channels (VCs). Current focusing (e.g tripolar stimulation) has been proposed to reduce current spread and thereby reduce interactions. In this study, current steering and current focusing were combined in a four-electrode stimulation pattern, i.e quadrupolar virtual channels (QPVCs). The spread of excitation was measured and compared between QPVC and Monopolar VC (MPVC) stimuli using a forward masking task. Results showed a sharper peak in the excitation pattern and reduced spread of masking for QPVC stimuli. Results from the forward masking study were compared with a previous study measuring VC discrimination ability and showed a weak relationship between spread of excitation and VC discriminability. The results suggest that CI signal processing strategies that utilize both current steering and current focusing might increase CI users' functional spectral resolution by transmitting more channels and reducing channel interactions.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cochlear-implant spatial selectivity with monopolar, bipolar and tripolar stimulation.Hear Res. 2012 Jan;283(1-2):45-58. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2011.11.005. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Hear Res. 2012. PMID: 22138630 Free PMC article.
-
Loudness and pitch perception using Dynamically Compensated Virtual Channels.Hear Res. 2017 Feb;344:223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2016.11.017. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Hear Res. 2017. PMID: 27939418 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction in spread of excitation from current focusing at multiple cochlear locations in cochlear implant users.Hear Res. 2016 Mar;333:98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Hear Res. 2016. PMID: 26778546 Free PMC article.
-
Cochlear infrastructure for electrical hearing.Hear Res. 2011 Nov;281(1-2):65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2011.05.002. Epub 2011 May 14. Hear Res. 2011. PMID: 21605648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limitations on Temporal Processing by Cochlear Implant Users: A Compilation of Viewpoints.Trends Hear. 2025 Jan-Dec;29:23312165251317006. doi: 10.1177/23312165251317006. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Trends Hear. 2025. PMID: 40095543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial channel interactions in cochlear implants.J Neural Eng. 2011 Aug;8(4):046029. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/8/4/046029. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Neural Eng. 2011. PMID: 21750370 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing current spread using current focusing in cochlear implant users.Hear Res. 2012 Feb;284(1-2):16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2011.12.009. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Hear Res. 2012. PMID: 22230370 Free PMC article.
-
Improving speech perception in noise with current focusing in cochlear implant users.Hear Res. 2013 May;299:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23467170 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pulse phase duration on forward masking and spread of excitation in cochlear implant listeners.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 20;15(7):e0236179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236179. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32687516 Free PMC article.
-
Current steering with partial tripolar stimulation mode in cochlear implants.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2013 Apr;14(2):213-31. doi: 10.1007/s10162-012-0366-8. Epub 2012 Dec 19. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23250685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas PJ, Hughes ML, Brown CJ, Miller CA, South H. Channel interaction in cochlear implant users evaluated using the electrically evoked compound action potential. Audiol Neurootol. 2004;9:203–13. Cohen 2003. - PubMed
-
- Berenstein CK, Mens LHM, Mulder JJS, Vanpouke FJ. Current steering and current focusing in cochlear implants: comparison of monopolar, tripolar, and virtual channel electrode configurations. Ear Hear. 2008;29:250–260. - PubMed
-
- Bierer JA, Middlebrooks JC. Auditory cortical images of cochlear-implant stimuli: dependence on electrode configuration. J Neurophysiol. 2002;87:478–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

