A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration
- PMID: 20851191
- PMCID: PMC3065962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.025
A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration
Abstract
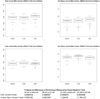
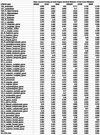
The United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) commit significant support to open-source data and software resources in order to foment reproducibility in the biomedical imaging sciences. Here, we report and evaluate a recent product of this commitment: Advanced Neuroimaging Tools (ANTs), which is approaching its 2.0 release. The ANTs open source software library consists of a suite of state-of-the-art image registration, segmentation and template building tools for quantitative morphometric analysis. In this work, we use ANTs to quantify, for the first time, the impact of similarity metrics on the affine and deformable components of a template-based normalization study. We detail the ANTs implementation of three similarity metrics: squared intensity difference, a new and faster cross-correlation, and voxel-wise mutual information. We then use two-fold cross-validation to compare their performance on openly available, manually labeled, T1-weighted MRI brain image data of 40 subjects (UCLA's LPBA40 dataset). We report evaluation results on cortical and whole brain labels for both the affine and deformable components of the registration. Results indicate that the best ANTs methods are competitive with existing brain extraction results (Jaccard=0.958) and cortical labeling approaches. Mutual information affine mapping combined with cross-correlation diffeomorphic mapping gave the best cortical labeling results (Jaccard=0.669±0.022). Furthermore, our two-fold cross-validation allows us to quantify the similarity of templates derived from different subgroups. Our open code, data and evaluation scripts set performance benchmark parameters for this state-of-the-art toolkit. This is the first study to use a consistent transformation framework to provide a reproducible evaluation of the isolated effect of the similarity metric on optimal template construction and brain labeling.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Acosta-Cabronero J, Williams GB, Pereira JMS, Pengas G, Nestor PJ. The impact of skull-stripping and radio-frequency bias correction on grey-matter segmentation for voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage. 2008 Feb;39(4):1654–1665. - PubMed
-
- Ardekani BA, Guckemus S, Bachman A, Hoptman MJ, Wojtaszek M, Nierenberg J. Quantitative comparison of algorithms for inter-subject registration of 3D volumetric brain MRI scans. J Neurosci Methods. 2005 Mar;142(1):67–76. - PubMed
-
- Arnold VI. Ordinary Differential Equations. Springer-Verlag; 1991.
-
- Ashburner J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. Neuroimage. 2007 Oct;38(1):95–113. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston K. Voxel-based morphometry—The methods. Neuroimage. 2000;11:805–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

