A practical method for transforming free-text eligibility criteria into computable criteria
- PMID: 20851207
- PMCID: PMC3129371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbi.2010.09.007
A practical method for transforming free-text eligibility criteria into computable criteria
Abstract
Formalizing eligibility criteria in a computer-interpretable language would facilitate eligibility determination for study subjects and the identification of studies on similar patient populations. Because such formalization is extremely labor intensive, we transform the problem from one of fully capturing the semantics of criteria directly in a formal expression language to one of annotating free-text criteria in a format called ERGO annotation. The annotation can be done manually, or it can be partially automated using natural-language processing techniques. We evaluated our approach in three ways. First, we assessed the extent to which ERGO annotations capture the semantics of 1000 eligibility criteria randomly drawn from ClinicalTrials.gov. Second, we demonstrated the practicality of the annotation process in a feasibility study. Finally, we demonstrate the computability of ERGO annotation by using it to (1) structure a library of eligibility criteria, (2) search for studies enrolling specified study populations, and (3) screen patients for potential eligibility for a study. We therefore demonstrate a new and practical method for incrementally capturing the semantics of free-text eligibility criteria into computable form.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


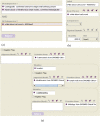
 button allows the creation of a new comparison ERGO Annotation as shown in Figure 3 (b) or a new noun phrase ERGO Annotation as shown in Figure 3 (c). Figure 3 (c). A possible user-interface for specifying a noun phrase such as “Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymph nodes, confirmed histologically,” initially consisting of a primitive noun and its adjectival modifiers. By clicking on the “More” button, a user can specify additional modifier attributes and noun phrases. Tool support can easily facilitate the task of searching terminological references such as primitive nouns and adjectival modifiers.
button allows the creation of a new comparison ERGO Annotation as shown in Figure 3 (b) or a new noun phrase ERGO Annotation as shown in Figure 3 (c). Figure 3 (c). A possible user-interface for specifying a noun phrase such as “Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymph nodes, confirmed histologically,” initially consisting of a primitive noun and its adjectival modifiers. By clicking on the “More” button, a user can specify additional modifier attributes and noun phrases. Tool support can easily facilitate the task of searching terminological references such as primitive nouns and adjectival modifiers.

References
-
- Campbell MK, Snowdon C, Francis D, Elbourne D, McDonald AM, Knight R, et al. Recruitment to randomised trials: strategies for trial enrollment and participation study. The STEPS study. Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(48):iii, ix–105. - PubMed
-
- Boissel JP, Amsallem E, Cucherat M, Nony P, Haugh MC. Bridging the gap between therapeutic research results and physician prescribing decisions: knowledge transfer, a prerequisite to knowledge translation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Nov;60(9):609–16. - PubMed
-
- OWL Working Group OWL 2 Web Ontology Language: Structural Specification and Functional-Style Syntax. 2009
-
- Niland J. ASPIRE: Agreement on Standardized Protocol Inclusion Requirements for Eligibility. 2007 [cited 2008 August 20]; Available from: http://hsspcohort.wikispaces.com/space/showimage/ASPIRE+CDISC+Intrachang....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

