Patients with celiac disease and B-cell lymphoma have a better prognosis than those with T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 20851210
- PMCID: PMC3594736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.09.007
Patients with celiac disease and B-cell lymphoma have a better prognosis than those with T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background & aims: Celiac disease (CD) is associated with an increased risk of lymphoma. However, relatively few studies have assessed the outcome of patients diagnosed with both CD and lymphoma. We evaluated the temporal association between lymphoma and CD, along with clinical presentation, response to therapy, and prognosis.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with both CD and lymphoma were identified retrospectively in a tertiary referral center. Clinical characteristics and survival were analyzed.
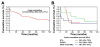
Results: Sixty-three patients (36 men) were identified who had been diagnosed with lymphoma and CD. Thirty-six (57%) were diagnosed with CD before they were diagnosed with lymphoma. The most common histologic entity was diffuse, large, B-cell lymphoma, which affected 18 (29%) patients. Complete information for staging was available in 59 patients; 24 (38%) had stage IV disease. Only chemotherapy or only radiation therapy was used for 43 (68%) and 11 (17%) patients, respectively. The 5- and 10-year cumulative survival rates for the entire cohort were 58% and 39%, respectively. Survival of patients with T-cell lymphoma was shorter than for all other lymphomas (119.4 vs 22.8 mo; P = .02).
Conclusions: CD is associated with B- and T-cell lymphomas. Patients with B-cell lymphomas had a better prognosis than those with T-cell lymphoma. Therapy is unsatisfactory for enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma.
Copyright © 2010 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primary colon lymphoma in Korea: a KASID (Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases) Study.Dig Dis Sci. 2005 Dec;50(12):2243-7. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-3041-7. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. PMID: 16416168
-
Malignant lymphomas in coeliac disease: evidence of increased risks for lymphoma types other than enteropathy-type T cell lymphoma.Gut. 2005 Jan;54(1):54-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.032094. Gut. 2005. PMID: 15591504 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of three subtypes of primary sinonasal lymphoma characterized by immunophenotypic analysis.Head Neck. 2004 Jul;26(7):584-93. doi: 10.1002/hed.20015. Head Neck. 2004. PMID: 15229900
-
Sinonasal lymphoma: case series and review of the literature.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014 Aug;4(8):670-4. doi: 10.1002/alr.21337. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014. PMID: 24760602 Review.
-
Enteropathy-Associated T cell Lymphoma.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2021 Apr;16(2):140-147. doi: 10.1007/s11899-021-00634-4. Epub 2021 May 19. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2021. PMID: 34009525 Review.
Cited by
-
Does celiac disease influence survival in lymphoproliferative malignancy?Eur J Epidemiol. 2013 Jun;28(6):475-83. doi: 10.1007/s10654-013-9789-8. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Eur J Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23463575 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant complications of celiac disease: a case series and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2022 Dec 12;16(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s13256-022-03682-3. J Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36503568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EBV-Associated Lymphoproliferative Disorder and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Patient with Severe Celiac Disease.Case Rep Hematol. 2018 Mar 5;2018:6063519. doi: 10.1155/2018/6063519. eCollection 2018. Case Rep Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29692937 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of malignant neoplasms in celiac disease patients - a nationwide United States population-based study.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Aug 24;15(8):1048-1060. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i8.1048. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39193153 Free PMC article.
-
Malignancies in Celiac Disease-A Hidden Threat with Diagnostic Pitfalls.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 19;13(6):1507. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061507. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Green PH, Cellier C. Celiac disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1731–1743. - PubMed
-
- Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:286–292. - PubMed
-
- Maki M, Mustalahti K, Kokkonen J, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease among children in Finland. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2517–2524. - PubMed
-
- Rostom A, Murray JA, Kagnoff MF. American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute technical review on the diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:1981–2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical